4 Operational
4.3 Commissioning with control signal terminals (default settings)
DC1…20… and DC1…OE1 Variable Frequency Drives
02/20 MN040059EN
www.eaton.com
125
▶
You can now set the output frequency (0 - 50 Hz) and, as a result, the
speed of the connected three-phase motor (0 - n
Motor
), by using the
potentiometer via terminal 6 (0 - +10 V proportional voltage signal).
Output frequency changes will be delayed based on the specified
acceleration and deceleration times. When using the device’s default
settings, these times will be set to 5 seconds.
The acceleration and deceleration ramps specify the time change for the
output frequency: from 0 to f
max
(WE = 50 Hz) or from f
max
back to 0.
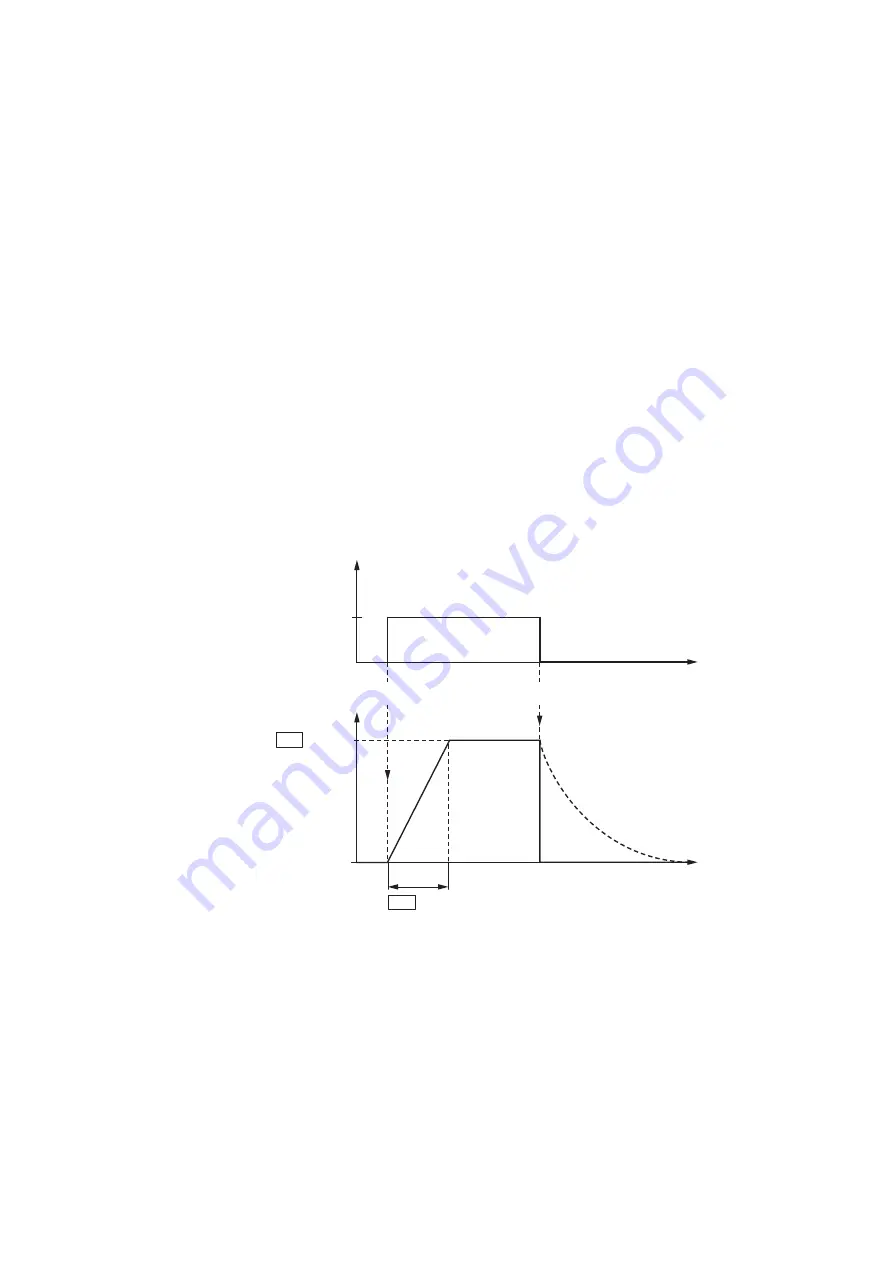
Figure 73 shows an example illustrating the time response when a RUN
enable signal (FWD or REV) is switched on while the maximum setpoint
voltage (+10 V) is being applied at control signal terminal 6. The speed of the
motor follows the output frequency, depending on the load torque and
moment of inertia (slip), from zero to n
max
.
The acceleration time is set in parameter P-03.
If the enable signal (FWD or REV) is switched off during operation, the
inverter will be disabled immediately (STOP) and the output frequency will be
set to zero. This will cause the motor to coast to a stop – see
①
below.
Figure 73:Start-Stop command with maximum reference voltage, acceleration ramp 5 s
t
t
f
max
~ n
max
f
P-03 = 5 s
FWD
REV
+24 V
= 50 Hz
0
P-07
①
RUN
STOP
















































