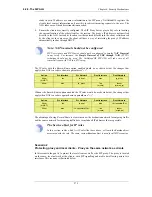
Figure 6.4. SMTP ALG Processing Order
Using Wildcards in White and Blacklists
Entries made in the white and blacklists can make use of wildcarding to have a single entry cover a
large number of potential email addresses. The wildcard character "*" can be used to represent any
sequence of characters.
For instance, the address entry *@some_domain.com can be used to specify all possible email
addresses for some_domain.com.
If, for example, wildcarding is used in the blacklist to block all addresses for a certain company
called my_company then the blacklist address entry required could be *@my_company.com.
If we want to now explicitly allow mails for just one department called my_department in
my_company then this could be done with an entry in the whitelist of the form
my_department@my_company.com.
Enhanced SMTP and Extensions
Enhanced SMTP (ESMTP) is defined in RFC 1869 and allows a number extensions to the standard
SMTP protocol.
When an SMTP client opens a session with an SMTP server using ESMTP, the client first sends an
EHLO command. If the server supports ESMTP it will respond with a list of the extensions that it
supports. These extensions are defined by various separate RFCs. For example, RFC 2920 defines
the SMTP Pipelining extension. Another common extension is Chunking which is defined in RFC
3030.
The NetDefendOS SMTP ALG does not support all ESMTP extensions including Pipelining and
Chunking. The ALG therefore removes any unsupported extensions from the supported extension
list that is returned to the client by an SMTP server behind the NetDefend Firewall. When an
extension is removed, a log message is generated with the text:
unsupported_extension
capability_removed
The parameter "capa=" in the log message indicates which extension the ALG removed from the
server response. For example, this parameter may appear in the log message as:
6.2.5. The SMTP ALG
Chapter 6. Security Mechanisms
261
Содержание DFL-1600 - Security Appliance
Страница 27: ...1 3 NetDefendOS State Engine Packet Flow Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 27 ...
Страница 79: ...2 7 3 Restore to Factory Defaults Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 79 ...
Страница 146: ...3 9 DNS Chapter 3 Fundamentals 146 ...
Страница 227: ...4 7 5 Advanced Settings for Transparent Mode Chapter 4 Routing 227 ...
Страница 241: ...5 4 IP Pools Chapter 5 DHCP Services 241 ...
Страница 339: ...6 7 Blacklisting Hosts and Networks Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 339 ...
Страница 360: ...7 4 7 SAT and FwdFast Rules Chapter 7 Address Translation 360 ...
Страница 382: ...8 3 Customizing HTML Pages Chapter 8 User Authentication 382 ...
Страница 386: ... The TLS ALG 9 1 5 The TLS Alternative for VPN Chapter 9 VPN 386 ...
Страница 439: ...Figure 9 3 PPTP Client Usage 9 5 4 PPTP L2TP Clients Chapter 9 VPN 439 ...
Страница 450: ...9 7 6 Specific Symptoms Chapter 9 VPN 450 ...
Страница 488: ...10 4 6 Setting Up SLB_SAT Rules Chapter 10 Traffic Management 488 ...
Страница 503: ...11 6 HA Advanced Settings Chapter 11 High Availability 503 ...
Страница 510: ...12 3 5 Limitations Chapter 12 ZoneDefense 510 ...
Страница 533: ...13 9 Miscellaneous Settings Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 533 ...