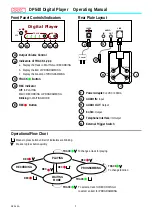
GLOSSARY
DESCRIPTION
AC-3
Digital coding of one to six channels (5 plus 1) in a bitstream. Compare Dolby Digital.
Bit
"Binary Digit”. A bit is the smallest information unit in the EDV as well as in digital transmission
systems. Bit is the indication for the height of the resolution in the uncompressed PCM size.
Cinch-Audio
Over the Cinch sockets, the Dolby-Digital or MPEG sound will be released from the DVD as
analogue two-channel signal - independent from the channel number on the DVD. If a DVD
plays with DTS sound, the output will be silent. In this case you must connect a stereo system
or an analogue surround amplifier/receiver. Using some DVD-Players, you must activate the
Stereo-Cinch output in the setup menu (Option: "Audio output/2-channel-analogue”).
Cinch-Video
The DVD-Player sends the Composite or FBAS video signal over the yellow Cinch socket,
either directly to the corresponding socket on the TV or indirectly over an AV receiver. Cinch is
the qualitatively worst picture connection and should only be used if there is no other option.
Components Output
Component signals of the DVD-Player are indigestible for customary TV's. Only tube
projectors and a few professional monitors have an input for the integration of picture
signals (also named YUV). The components output provides the best picture quality.
Digital Output
The Player releases its sound information bit by bit over the digital output. The way the sound
will stream out of the socket must be adjusted in the setup menu. Most important criteria:
Which device is connected to the digital socket?
Dolby Digital
A digital surround sound system which is able to transfer up to 5 sound channels plus sub-
bass channel (5.1 or 3/2.01). Developed by Dolby. Here, it is laid down, which sound signal
will be released from the digital output. "Bitstream” is the right choice, if the Player is connec-
ted to a Dolby-Digital decoder. "PCM” shall be entered, if the sound is lead via digital output on
a system without AC-3 decoder.
DTS
Digital Theatre Systems. Digital surround sound system, which works with 5.1 channels and
corresponds to AC-3 on the first view. It differs regarding the data reduction. The DTS system
works with higher data rates, i.e lower data reduction. It transfers about 4 times as much data
as the AC-3 or MPEG-2 process and therefore needs appreciable more storage space on the
DVD.
DTS (on/off)
On: Only if the Player is connected to an amplifier or receiver with DTS-Decoder. At the
moment, only some DVD-Players provide a conversion of the DTS multi-channel-sound into a
stereo signal.
FBAS
It is the most popular kind of transmission for colourful video pictures with only one wire. A
good resolution is basically possible, but it requires a lot of decoding efforts. Better is Y/C,
RGB or YUV.
5.1 Output
DVD-Players with digital surround decoder provide this output, the most current AV receiver
provide also the corresponding 5.1 input. Here the Player releases the already decoded multi-
channel sound from the DVD in an analogue way. But this connection is only useful if the AV
amplifier has no digital surround decoder. The sound quality over a digital surround amplifier is
in most cases better.
KHz
Kilocycle. kHz is the indication for the height of the scanning rate with which an analogue sig-
nal (PCM) is interrogated for the following Analogue/Digital transformation.
Letterbox
Transmission of a wide-screen film with bars on top and on bottom.
LPCM
Linear PCM. Description of the PCM sound of DVD's, corresponds to the CD system,
but with a higher reading rate (48kHz, 96kHz also possible).
NTSC
National Television System Committee, television norm among others in the USA and Japan
(from 525 lines only 480 lines will be transferred with a picture changing frequency of 60 half
pictures per second).
PAL
Phase Alternation Line, television norm in Germany and other European countries (from 625
lines only 576 lines will be transferred with a picture changing frequency of 50 half pictures per
second).
Pan & Scan
Full-page picture transmission of a wide-screen film on video by moving the sector for the 4:3
screen, when the focus of the happening shifts.
TECHNICAL TERMS
27