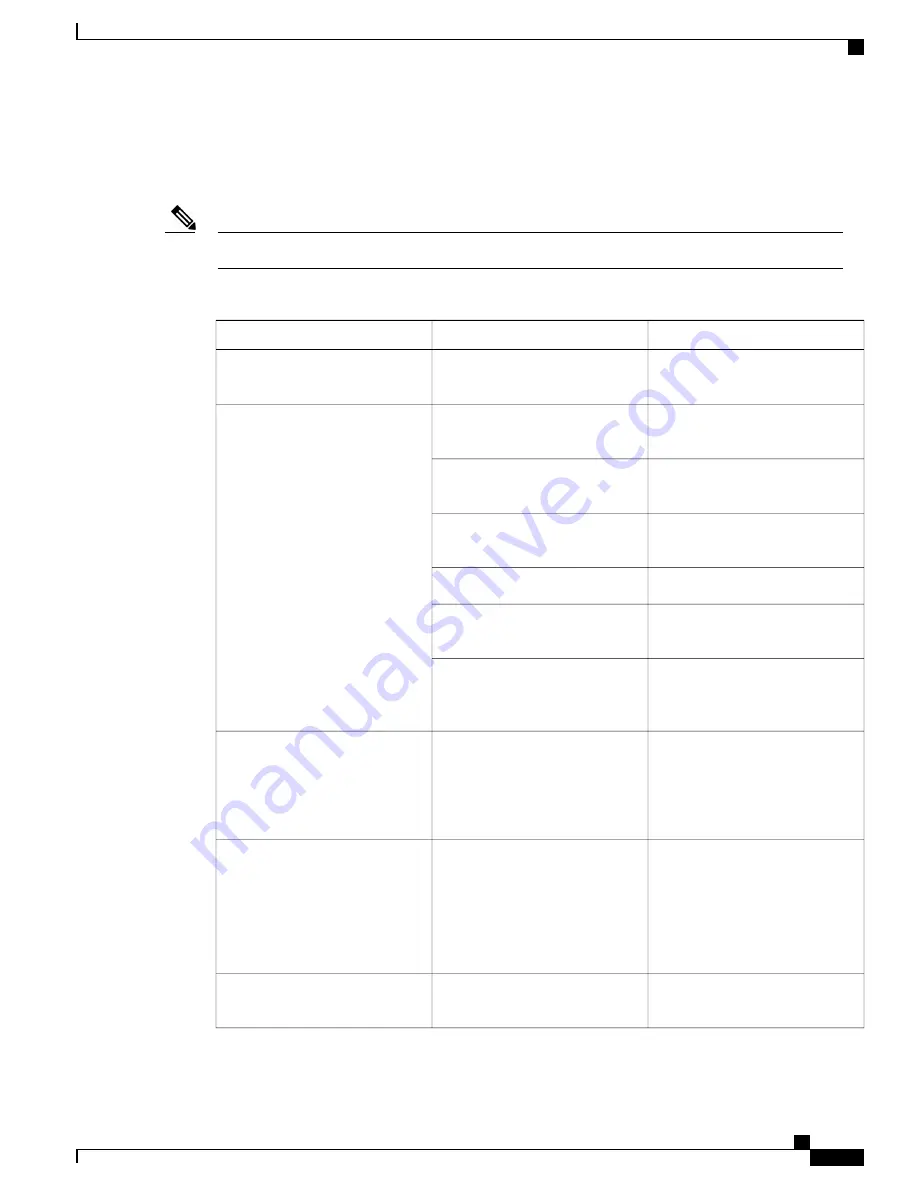
Editing Commands through Keystrokes
This table shows the keystrokes that you need to edit command lines. These keystrokes are optional.
The arrow keys function only on ANSI-compatible terminals such as VT100s.
Note
Table 5: Editing Commands through Keystrokes
Purpose
Keystroke
Capability
Moves the cursor back one
character.
Press
Ctrl-B
, or press the left
arrow key.
Move around the command line to
make changes or corrections.
Moves the cursor forward one
character.
Press
Ctrl-F
, or press the right
arrow key.
Moves the cursor to the beginning
of the command line.
Press
Ctrl-A
.
Moves the cursor to the end of the
command line.
Press
Ctrl-E
.
Moves the cursor back one word.
Press
Esc B
.
Moves the cursor forward one
word.
Press
Esc F
.
Transposes the character to the left
of the cursor with the character
located at the cursor.
Press
Ctrl-T
.
Recalls the most recent entry in the
buffer.
Press
Ctrl-Y.
Recall commands from the buffer
and paste them in the command
line. The switch provides a buffer
with the last ten items that you
deleted.
Recalls the next buffer entry.
The buffer contains only the last
10 items that you have deleted or
cut. If you press
Esc Y
more than
ten times, you cycle to the first
buffer entry.
Press
Esc Y
.
Erases the character to the left of
the cursor.
Press the
Delete
or
Backspace
key.
Delete entries if you make a
mistake or change your mind.
Layer 2/3 Command Reference, Cisco IOS XE Release 3E (Cisco WLC 5700 Series)
OL-32323-01
7
Using the Command-Line Interface
Using Editing Features






























