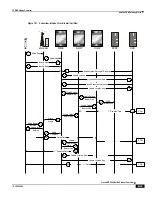
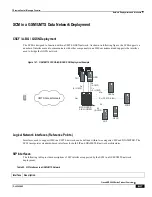
Session Control Manager Overview
Product Description ▀
Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview ▄
OL-22938-02
Telephony Application Server (TAS) Basic Supported
The following describe the local basic call features implemented on the S-CSCF:
Abbreviated Dialing (AD)
Call Forward Busy Line (CFBL)
Call Forward No Answer (CFNA)
Call Forward Not Registered (CFNR)
Call Forward Unconditional (CFU)
Call Transfer
Call Waiting
Caller ID Display (CID)
Caller ID Display Blocked (CIDB)
Feature Code Activation/De-activation
Follow Me/Find Me
Locally Allowed Abbreviated Dialing
Outbound Call Restrictions/Dialing Permissions
Short Code Dialing
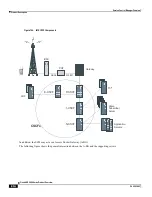
Integrated S/I-CSCF
The following Interrogating-CSCF features are supported for the integrated S/I-CSCF:
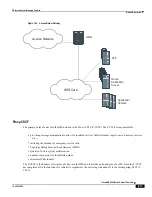
Assign an S-CSCF to a User Performing SIP Registration
- On a UE registration, the I-CSCF carries out a
first step authorization and S-CSCF discovery. For this, the I-CSCF sends a Cx User-Authentication-Request
(UAR) to the HSS by transferring the Public and Private User Identities and the visited network identifier (all
extracted from the UE REGISTER message). The HSS answers with a Cx User-Authentication-Answer
(UAA). The UAA includes the URI of the S-CSCF already allocated to the user. If there is no previously
allocated S-CSCF, the HSS returns a set of S-CSCF capabilities that the I-CSCF uses to select the S-CSCF.
E.164 Address Translation
- Translates the E.164 address contained in all Request-URIs having the SIP URI
with user=phone parameter format into the Tel: URI format before performing the HSS Location Query. In the
event the user does not exist, and if configured by operator policy, the I-CSCF may invoke the portion of the
transit functionality that translates the E.164 address contained in the Request-URI of the Tel: URI format to a
routable SIP URI.
Obtain the S-CSCF Address from the HSS
- When the I-CSCF receives a SIP request from another network, it
has to route the request to the called party. For this it obtains the S-CSCF address associated with the called
party from the HSS by querying with a Cx Location-Information-Request (LIR) message. The Public-Identity
AVP in the LIR is the Request-URI of the SIP request. The Location-Information-Answer (LIA) message
contains the S-CSCF address in the Server-Name AVP. The request is then routed to the S-CSCF.
Route a SIP Request or Forward Response from Another Network
- When the I-CSCF receives a request
from another network, it obtains the address of the S-CSCF from the HSS using the procedure detailed above
and routes the request to the S-CSCF. Responses are also routed to the S-CSCF.
Содержание ASR 5000 Series
Страница 1: ......
Страница 26: ......
Страница 48: ...New In Release 10 0 SCM Features Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 50: ......
Страница 58: ......
Страница 67: ...Product Service and Feature Licenses Default Licenses Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 68: ......
Страница 126: ......
Страница 138: ......
Страница 146: ......
Страница 218: ......
Страница 236: ......
Страница 356: ......
Страница 374: ......
Страница 422: ......
Страница 496: ......
Страница 572: ......
Страница 654: ......
Страница 700: ......
Страница 726: ......
Страница 784: ......
Страница 816: ......
Страница 839: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 841: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 844: ......
Страница 906: ......
Страница 926: ......
Страница 942: ......
Страница 943: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 30 Technical Specifications ...
Страница 966: ......
Страница 967: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 31 Safety Electrical and Environmental Certifications ...
Страница 972: ......