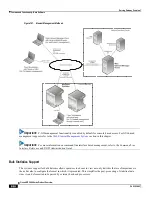
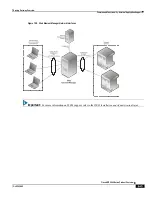
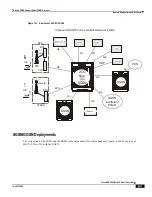
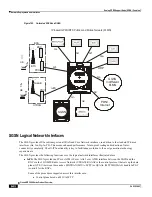
Serving Gateway Overview
▀ How the Serving Gateway Works
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview
OL-22938-02
Table 84.
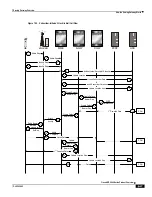
Subscriber-initiated Attach (initial) Call Flow Description
Step
Description
1
The UE initiates the Attach procedure by the transmission of an Attach Request (IMSI or old GUTI, last visited TAI (if
available), UE Network Capability, PDN Address Allocation, Protocol Configuration Options, Attach Type) message
together with an indication of the Selected Network to the eNodeB. IMSI is included if the UE does not have a valid GUTI
available. If the UE has a valid GUTI, it is included.
2
The eNodeB derives the MME from the GUTI and from the indicated Selected Network. If that MME is not associated
with the eNodeB, the eNodeB selects an MME using an ―MME selection function‖. The eNodeB forwards the Attach
Request message to the new MME contained in a S1-MME control message (Initial UE message) together with the
Selected Network and an indication of the E-UTRAN Area identity, a globally unique E-UTRAN ID of the cell from where
it received the message to the new MME.
3
If the UE is unknown in the MME, the MME sends an Identity Request to the UE to request the IMSI.
4
The UE responds with Identity Response (IMSI).
5
If no UE context for the UE exists anywhere in the network, authentication is mandatory. Otherwise this step is optional.
However, at least integrity checking is started and the ME Identity is retrieved from the UE at Initial Attach. The
authentication functions, if performed this step, involves AKA authentication and establishment of a NAS level security
association with the UE in order to protect further NAS protocol messages.
6
The MME sends an Update Location (MME Identity, IMSI, ME Identity) to the HSS.
7
The HSS sends Insert Subscriber Data (IMSI, Subscription Data) message to the MME. The Subscription Data contains the
list of all APNs that the UE is permitted to access, an indication about which of those APNs is the Default APN, and the
'EPS subscribed QoS profile' for each permitted APN.
8
The MME validates the UE's presence in the (new) TA. If due to regional subscription restrictions or access restrictions the
UE is not allowed to attach in the TA, the MME rejects the Attach Request with an appropriate cause, and may return an
Insert Subscriber Data Ack message to the HSS. If subscription checking fails for other reasons, the MME rejects the
Attach Request with an appropriate cause and returns an Insert Subscriber Data Ack message to the HSS including an error
cause. If all checks are successful then the MME constructs a context for the UE and returns an Insert Subscriber Data Ack
message to the HSS. The Default APN shall be used for the remainder of this procedure.
9
The HSS acknowledges the Update Location message by sending an Update Location Ack to the MME. If the Update
Location is rejected by the HSS; the MME rejects the Attach Request from the UE with an appropriate cause.
10
The MME selects an S-GW using ―Serving GW selection function‖ and allocates an EPS Bearer Identity for the Default
Bearer associated with the UE. If the PDN subscription context contains no P-GW address the MME selects a P-GW as
described in clause ―PDN GW selection function‖. Then it sends a Create Default Bearer Request (IMSI, MME Context ID,
APN, RAT type, Default Bearer QoS, PDN Address Allocation, AMBR, EPS Bearer Identity, Protocol Configuration
Options, ME Identity, User Location Information) message to the selected S-GW.
11
The S-GW creates a new entry in its EPS Bearer table and sends a Create Default Bearer Request (IMSI, APN, S-GW
Address for the user plane, S-GW TEID of the user plane, S-GW TEID of the control plane, RAT type, Default Bearer
QoS, PDN Address Allocation, AMBR, EPS Bearer Identity, Protocol Configuration Options, ME Identity, User Location
Information) message to the P-GW.
12
If dynamic PCC is deployed, the P-GW interacts with the PCRF to get the default PCC rules for the UE. The IMSI, UE IP
address, User Location Information, RAT type, AMBR are provided to the PCRF by the P-GW if received by the previous
message.
Содержание ASR 5000 Series
Страница 1: ......
Страница 26: ......
Страница 48: ...New In Release 10 0 SCM Features Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 50: ......
Страница 58: ......
Страница 67: ...Product Service and Feature Licenses Default Licenses Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 68: ......
Страница 126: ......
Страница 138: ......
Страница 146: ......
Страница 218: ......
Страница 236: ......
Страница 356: ......
Страница 374: ......
Страница 422: ......
Страница 496: ......
Страница 572: ......
Страница 654: ......
Страница 700: ......
Страница 726: ......
Страница 784: ......
Страница 816: ......
Страница 839: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 841: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 844: ......
Страница 906: ......
Страница 926: ......
Страница 942: ......
Страница 943: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 30 Technical Specifications ...
Страница 966: ......
Страница 967: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 31 Safety Electrical and Environmental Certifications ...
Страница 972: ......