Glossary
▀ Environmental Information
▄ Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview
OL-22938-02
Encapsulation.
The process of incorporating an original IP packet (less any preceding fields such as a MAC header)
inside another IP packet, making the fields within the original IP header temporarily lose their effect.
EPC Network
. Evolved packet core network. the successor to the 3GPP Release 7 packet-switched core network,
developed by 3GPP within the framework of the 3GPP System Architecture Evolution (SAE).
EPS. Evolved packet system
. The evolved packet system (EPS) or evolved 3GPP packet-switched domain consists of
the evolved packet core network and the evolved universal terrestrial radio access network.
Equivalent HPLMN list
. To allow provision for multiple HPLMN codes, PLMN codes that are present within this list
shall replace the HPLMN code derived from the IMSI for PLMN selection purposes. This list is stored on the USIM and
is known as the EHPLMN list. The EHPLMN list may also contain the HPLMN code derived from the IMSI. If the
HPLMN code derived from the IMSI is not present in the EHPLMN list then it shall be treated as a Visited PLMN for
PLMN selection purposes.
E-RAB identity
. the E-RABidentity uniquely identifies an E-RABfor one UE. Note. The E-RAB identity remains
unique for the UE even if the UE-associated logical S1-connection is released during periods of user inactivity.
E-RAB
. Eveloved Radio Access Bearer. An E-RAB uniquely identifies the concatenation of an S1 Bearer and the
corresponding Data Radio Bearer. When an E-RAB exists, there is a one-to-one mapping between this E-RAB and an
EPS bearer of the Non Access Stratum.
ESN.
Electronic Serial Number. A unique 32-bit binary number that identifies each cellular device. This information is
passed as part of the call setup.
EV-DO.
The second phase of CDMA2000 following 1xRTT deployment. 1xEV-DO stands for 1x Evolution - Data
Only, and is characterized by a maximum data rate of 2.4 Mbps.
F
FDMA.
Frequency Division Multiple Access. A method of allocating a discrete amount of frequency bandwidth to
individual users to allow multiple conversations across many users. The technique of assigning individual frequency
slots, and re-use of those slots throughout a system.
FITS. Failure in Time Statistics.
A statistical method of determining the number of failures that are expected to occur
over a specific time period. The telecommunications industry generally assumes this number to represent the number of
failures per million hours (Fpmh).
FEC.
Forward Error Correction. The physical link layer may add many extra bits to the data before transmitting it. The
receiving physical link layer uses those bits to automatically correct errors in the received data, without needing the data
to be retransmitted. The transmitter and receiver must use the same FEC algorithm.
Firewall.
A device that protects a private network against intrusion from nodes that are using the public network.
Flow Identifier.
An IP flow is indicated uniquely in an IMS session by means of a flow identifier. The flow identifier is
created based on the ordinal number of the media stream and of the IP flow in the media where the IP flows are
arranged based on the ports used.
Foreign Agent (FA).
A mobility agent on the foreign network that can assist the mobile node in receiving datagrams
delivered to the care-of address.
Foreign network.
The network to which the mobile node is attached when it is not attached to its home network, and on
which the care-of-address is reachable from the rest of the Internet.
Forward Tunnel.
The direction of encapsulated data traveling from the Home Agent to the Foreign Agent.
Frequency layer
. set of cells with the same carrier frequency.
FQDN. Fully qualified domain name.
An Internet node's FQDN is its complete domain name as defined by the
Domain Name System (DNS). A node can be known locally by a relative domain name that is a sub-string of its FQDN,
but such a relative name cannot be resolved correctly by Internet nodes outside of the part of the domain name hierarchy
indicated by the relative name. The fully qualified name can be resolved from anywhere in the Internet, subject to access
control and ability to route of the resolution request.
Содержание ASR 5000 Series
Страница 1: ......
Страница 26: ......
Страница 48: ...New In Release 10 0 SCM Features Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 50: ......
Страница 58: ......
Страница 67: ...Product Service and Feature Licenses Default Licenses Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 68: ......
Страница 126: ......
Страница 138: ......
Страница 146: ......
Страница 218: ......
Страница 236: ......
Страница 356: ......
Страница 374: ......
Страница 422: ......
Страница 496: ......
Страница 572: ......
Страница 654: ......
Страница 700: ......
Страница 726: ......
Страница 784: ......
Страница 816: ......
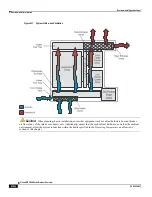
Страница 839: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 841: ...Network Address Translation Overview How NAT Works Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 ...
Страница 844: ......
Страница 906: ......
Страница 926: ......
Страница 942: ......
Страница 943: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 30 Technical Specifications ...
Страница 966: ......
Страница 967: ...Cisco ASR 5000 Series Product Overview OL 22938 02 Chapter 31 Safety Electrical and Environmental Certifications ...
Страница 972: ......