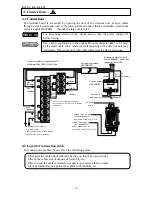
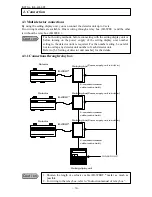
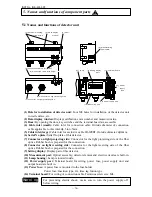
INST No INE -403-0P0
−
25
−
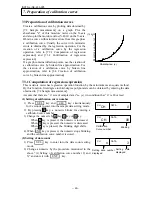
7. Preparation of calibration curves
The output characteristics of the moisture meter depend upon the measuring objects. Also, the
output characteristics may also change according to the process conditions and moisture
measurement conditions of samples for certain measuring objects.
Therefore, for accurate measurement of moisture, it is necessary to carry out the sample tests
of each measuring object in advance and obtain the relative relation (this is called as
calibration curve) between the moisture value (%H
2
O) obtained by the drying method or other
measuring methods and the absorbance "x" measured by the moisture meter This chapter
describes the measurement of the moisture value by the drying method. However, the method
of creation of the calibration curves is same even if the moisture value is measured by the
Karl Fischer method or other methods.
7.1 Sample preparation
7.1.1 Powder or granular
(1) Take a sample of about 2 to 4 liters from the measuring object.
(2) Dry up the sample up to the absolute dry condition by a dryer. Particularly be careful with
the heating temperature so as not to denature the sample.
(3) Divide the dry sample every 100 to 200cc into 5 to 6 samples separately, although it is
recommendable to divide the sample into many samples.
(4) Add water to these 5 to 6 samples bit by bit so that the moisture values of each sample
divides the measuring range almost evenly.
(5) Stir each sample with water addition sufficiently, and put it into a polyethylene bag and
seal it tightly.
(6) Leave each sample for about 2 days until its moisture is stabilized.
If a sample cannot be heated or if it is hardened by adding water and thus
can’t be measured, adjust the moisture correspondingly according to the
procedure in case of a paper shown below.
C a u t i o n
7. Preparation of calibration curves
1
2
3
N