ATLAS North America Proprietary
Sea Scan® ARC Explorer™ Manual
1 of 1
Page: 23
Issue: 4.2.1
2SFT1-0001
Manual
This new ability to "aim" the sonar beam at vertical structures requires a different approach when
operating the towfish. It will also require some advance planning and practice.
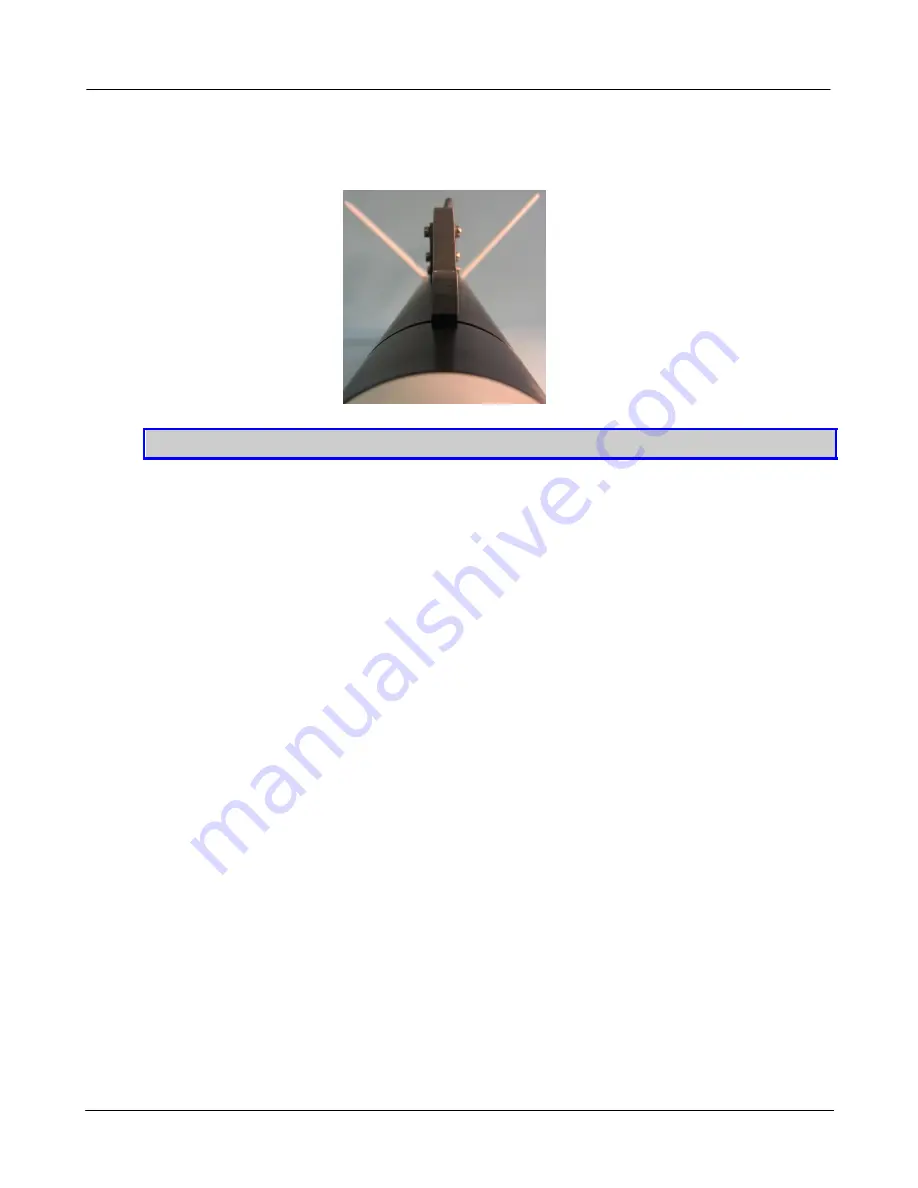
Figure 27: Towrail in the centered position
TIP:
Practice using the towfish at the normal angle before attempting a more complex survey.
The following procedures are recommended when using a different tow angle:
·
Tow from the bow (forward point of the vessel) to avoid prop wash (propeller turbulence). Midship
is an alternative, but the bow is preferred.
·
Allow only enough cable for the towfish to run at about 1- to 2 feet (30- to 61 cm) below the
surface of the water.
·
The towfish distance should be at approximately 10% standoff from the vertical surface.
·
Set the range in the software for the water depth.
·
Start with an angle of approximately 40° to 45°.
·
Closely observe the "grazing angle", the percentage of deviation from straight on at which the
sonar beam strikes the vertical or concave surface you are investigating.
4.2.3.1
Adjustment Procedure
Adjusting the Variable-Angle Towrail is an easy process.
·
Loosen the two screws located at the top of the towrail. The screws are captive, back them out
until they stop. Do not attempt to further back the screw out once it has stopped.
















































