Chapter 13 Spanning Tree Protocol
XMG1930 Series User’s Guide
152
13.5 Configure Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol
Use this screen to configure RSTP settings, see
for more information on RSTP.
Click
RSTP
in the
Advanced Application
>
Spanning Tree Protocol
screen.
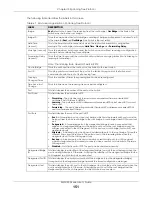
Figure 109
Advanced Application > Spanning Tree Protocol > RSTP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
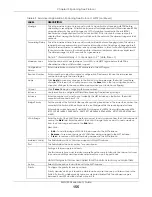
Table 68 Advanced Application > Spanning Tree Protocol > RSTP
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Status
Click
Status
to display the
RSTP
Status
screen.
Active
Select this check box to activate RSTP. Clear this check box to disable RSTP.
Note: You must also activate
Rapid Spanning Tree
in the
Advanced Application
>
Spanning Tree Protocol
>
Configuration
screen to enable RSTP on the Switch.
Bridge Priority
Bridge priority is used in determining the root switch, root port and designated port. The Switch
with the highest priority (lowest numeric value) becomes the STP root switch. If all Switches
have the same priority, the Switch with the lowest MAC address will then become the root
switch. Select a value from the drop-down list box.
The lower the numeric value you assign, the higher the priority for this bridge.
Bridge Priority determines the root bridge, which in turn determines Hello Time, Max Age and
Forwarding Delay.
Hello Time
This is the time interval in seconds between BPDU (Bridge Protocol Data Units) configuration
message generations by the root switch. The allowed range is 1 to 10 seconds.
Max Age
This is the maximum time (in seconds) the Switch can wait without receiving a BPDU before
attempting to reconfigure. All Switch ports (except for designated ports) should receive BPDUs
at regular intervals. Any port that ages out STP information (provided in the last BPDU)
becomes the designated port for the attached LAN. If it is a root port, a new root port is
selected from among the Switch ports attached to the network. The allowed range is 6 to 40
seconds.