Chapter 8 Basic Setting
GS1350 Series User’s Guide
94
8.6 IP Setup
Use the
IP Setup
screen to configure the default gateway device, the default domain name server and
add IP domains.
8.6.1 IP Interfaces
The Switch needs an IP address for it to be managed over the network. When the Switch (in standalone
mode) fails to obtain an IP address from a DHCP server, the static IP address 192.168.1.1 will be
automatically added and used as the Switch’s management IP address.
On the Switch, an IP address is not bound to any physical ports. Since each IP address on the Switch
must be in a separate subnet, the configured IP address is also known as IP interface (or routing
domain). In addition, this allows routing between subnets based on the IP address without additional
routers.
You can configure multiple routing domains on the same VLAN as long as the IP address ranges for the
domains do not overlap. To change the IP address of the Switch in a routing domain, simply add a new
routing domain entry with a different IP address in the same subnet.
You can configure up to 64 IP domains which are used to access and manage the Switch from the ports
belonging to the pre-defined VLANs.
Note: You must configure a VLAN first. Each VLAN can have multiple management IP
addresses, and you can log into the Switch via different management IP addresses
simultaneously.
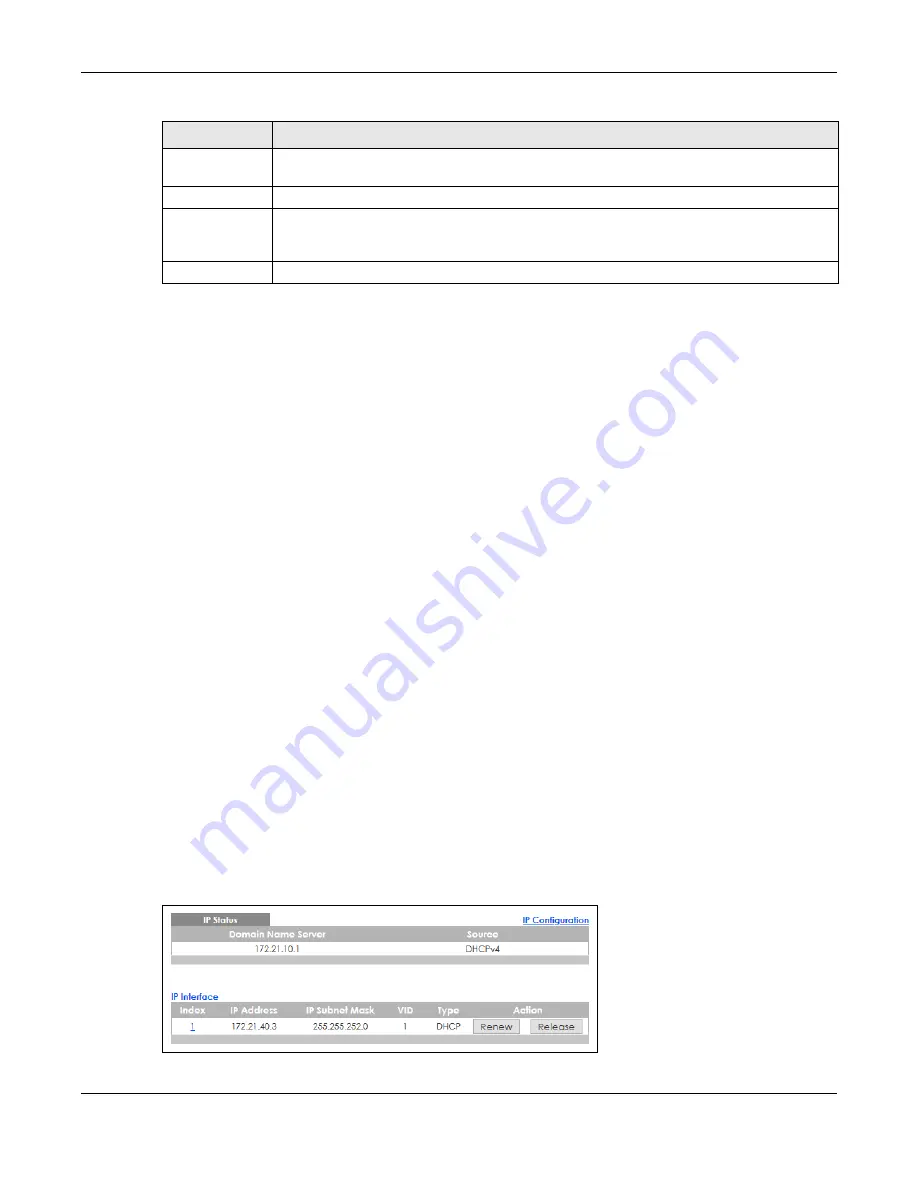
8.6.2 IP Status
Figure 71
Basic Setting > IP Setup
Priority 1
This is typically used for non-critical “background” traffic such as bulk transfers that are allowed
but that should not affect other applications and users.
Priority 0
Typically used for best-effort traffic.
Apply
Click
Apply
to save your changes to the Switch’s run-time memory. The Switch loses these
changes if it is turned off or loses power, so use the
Save
link on the top navigation panel to save
your changes to the non-volatile memory when you are done configuring.
Cancel
Click
Cancel
to reset the fields.
Table 26 Basic Setting > Switch Setup (continued)
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
















































