AF6ZP0AL - COMBIAC0 & ACE0 - User Manual
Page - 61/79
12.3 Analysis and troubleshooting of microcontroller alarms
To Enter the MAIN MENU’ push the Enter button at the Home Page of the hand
set display and Roll for the ALARMS item. Here is the ALARMS list:
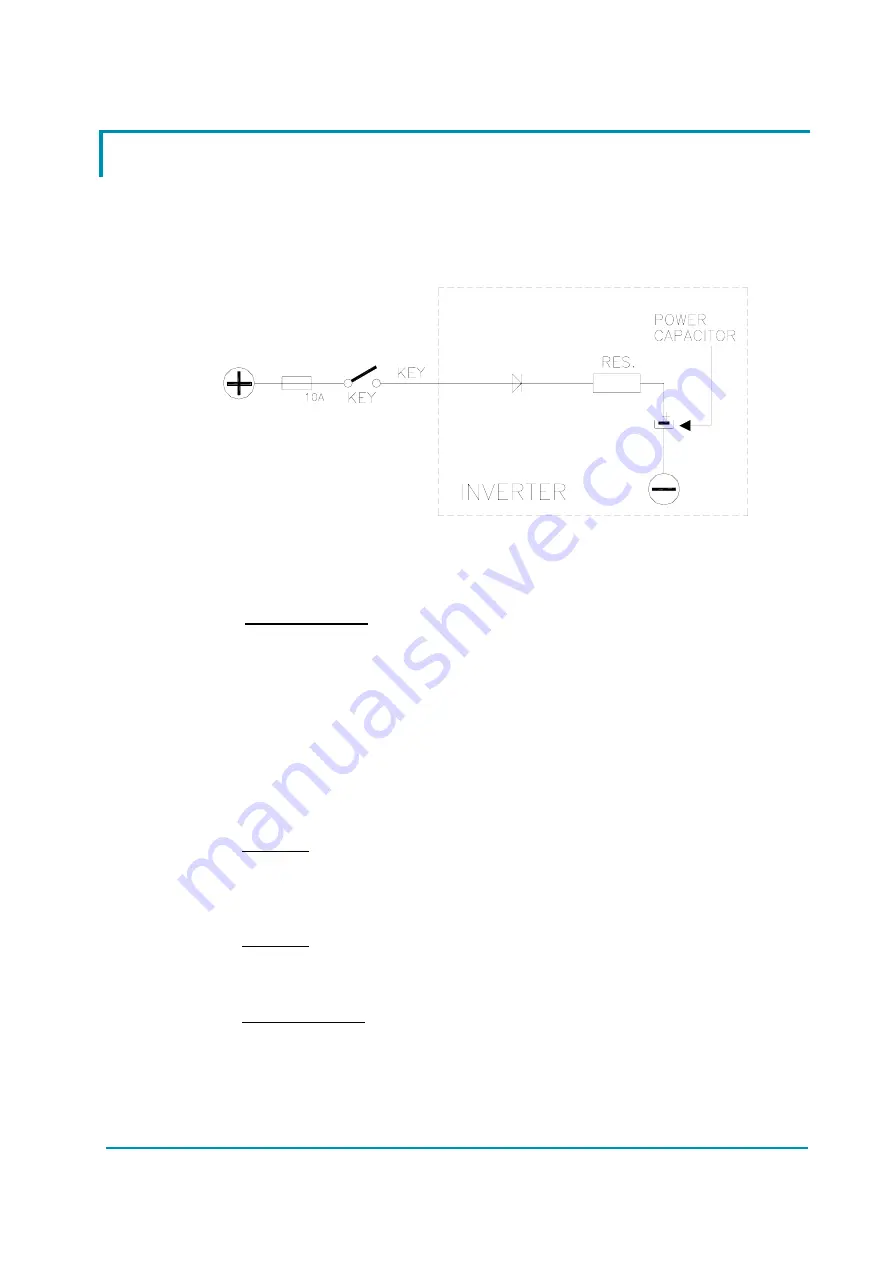
1) “CAPACITOR
CHARGE”
Follows the charging capacitor system:
When the key is switched ON, the inverter tries to charge the power
capacitors through a power resistance, and check if the capacitor are
charged within a timeout. If they do not charge, an alarm is signalled; the
main contactor is not closed.
Troubleshooting:
A) There is an external load in parallel to capacitor bank, which sinks current
from the controller capacitors precharging circuit, thus preventing the
caps from charging. Check if a lamp or a dc/dc converter or a auxiliary
load is placed in // to capacitor bank.
B) The charging resistance is opened; insert a power resistance across line
contactor power terminals; if the alarm disappears, it means the controller
internal charging resistance is damaged.
C) The charging circuit has a failure, inside the controller.
D) There is a problem in the controller power section.
2) “VMN
LOW”
Cause 1: start-up test.
Before switching the LC on, the software checks the power bridge: it turns on
alternatingly the High side Power Mosfets and expects the phases voltage to
increase toward the rail capacitor value. If the phases voltage does not
increase, this alarm occurs.
Cause 2:
Motor running test. When the motor is running, power bridge is ON, the motor
voltage feedback is tested; if it is lower than commanded value, fault status is
entered.
Troubleshooting:
A) If the problem occurs at start up (the LC does not close at all), check:
-
Motor internal connections (ohmic continuity)
-
Motor power cables connections
-
Motor leakage to truck frame
-
If the motor connections are OK, the problem is inside the controller
















































