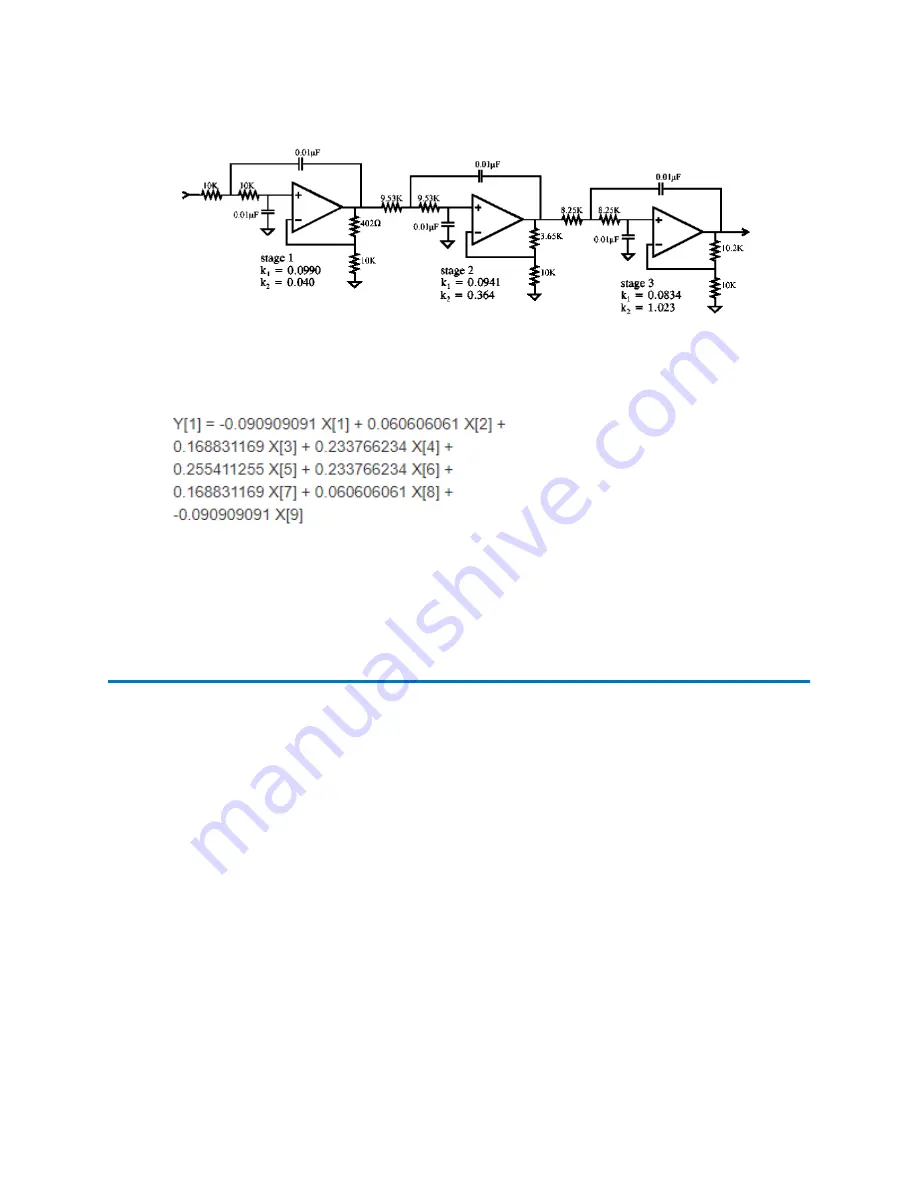
Figure 7–9: Analog 6-pole Bessel filter
A digital filter does not have poles, but it is characterized by the number of input data points used
to calculate a new output data point. For example, a 9-point digital filter (Savitzky-Golay) is given
as:
Note that the sum of coefficients is exactly 1. Y [n] is the output data point and X [n] are input
data points. Generally speaking, the performance of a digital filter improves with more input data
points, but greater processor capacity is required for the large number of calculations.
7.3 Applying ADF in chromatography
If noise frequencies in LC-EC differ from the frequency of the signal, noise can be suppressed.
Using the right filter setting (cutoff frequency) will specifically attenuate noise and improve the
signal-to-noise (S/N) ratio. No matter how advanced a filter is, it is only possible to apply low pass
filtering if noise frequencies are higher than the frequency of the signal.
December 16, 2021, 715007395 Ver. 00
Page 69
















































