DS1061-015B
7
2. SYSTEM DESIGN
2.1 NOTES FOR A CORRECT INSTALLATION
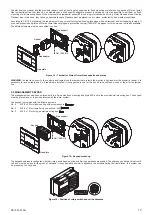
The.1061.control.panel.must.be.placed.in.a.position.protected.by.intrusion.detectors..If.it.is.needed.the.GSM.module.usage,.it.is.necessary.
to verify in advance if, in the selected position, the GSM signal is good. To check it, verify the field strength using the GSM coverage test (see
paragraph 5.4.11).
.
WARNING
:.
For GSM network coverage check, it is necessary to use the same mobile network carrier SIM as the one used in the GSM module.
This because in the same place, coverage levels of various mobile network carriers can be very different, or even absent.
.
Management.keypads,.electronic.key.readers.and.proximity.readers.must.be.put.in.dry.places,.protected.against.bad.weather.conditions..These.
devices are daisy chained to the control panel with a single bus cable. The sequence used to connect them to the bus is irrelevant (devices are
identified by a hardware address, not according to the connection sequence), so it is possible to use for the bus the most convenient and the
fastest.path.for.installation.
2.2 BATTERY DIMENSIONING
CEI 79-2 standards (and IMQ trademark) require for the system a battery endurance of 24 hours at least in case of mains fail. So, the control
panel.battery.must.be.designed.in.order.to.guarantee.that.range.
The.formula.to.calculate.the.battery.minimum.capacity.is.the.following:
C
b
= (I
r
x 24 x 1,25) + (I
a
x alarm duration x 0,02)
where:
.
C
b
.is.the.minimum.battery.capacity,.in.Ah
.
I
r
.is.the.total.consumption.in.standby.mode,.in.Ampere
.
I
a
.is.the.total.consumption.during.the.alarm,.in.Ampere
.
alarm duration
.is.the.programmed.alarm.duration,.in.minutes
This calculation must be done referring to all devices powered by the battery (current consumption of each device can be find in technical
sheets).
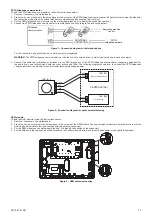
2.3 CABLE DIMENSIONING AND POSITIONING
2.3.1 DIMENSIONING
The cable cross section must be calculated considering the most critical system power supply condition, equivalent to mains fail and backup
battery just over the “flat battery” level (11,2V–). For example, if at full load conditions, on all the devices power supply terminals must be ensured
at.least.10,5V–,.the.maximum.voltage.dropout.admitted.on.the.cables.is.0,7V–.
The.calculation.formula.is:
V
c
= 2 x length x R
m
x I
d
where:
.
V
c
.is.the.voltage.dropout.in.Volt
.
length
is the cable length, in metres (single wire)
.
R
m
.is.the.cable.resistance.in.Ohm/m
.
I
d
.is the current required by the devices, in Ampere (value obtained by their technical sheets)
Copper.cables.resistance.values.are:
Section - mm
2
0,
0,50
0,75
1,00
1,50
Resistance - Ohm/m
0,0795
0,0350
0,033
0,0175
0,0117
The following diagram can be useful to find the minimum cable section that is necessary.
1,50 mmq
1,00 mmq
0,75 mmq
0,50 mmq
0,22 mmq
100
consumption (mA)
1,00
10,00
100,00
1000,00
cable length (m)
1000
900
800
700
600
500
400
300
200
Cable dimensioning
(with maximum voltage dropout of 0,7V)