9-9
Configuring Advanced Features
Stack Management
C
o
nf
ig
u
ring Adva
nc
ed
Featu
res
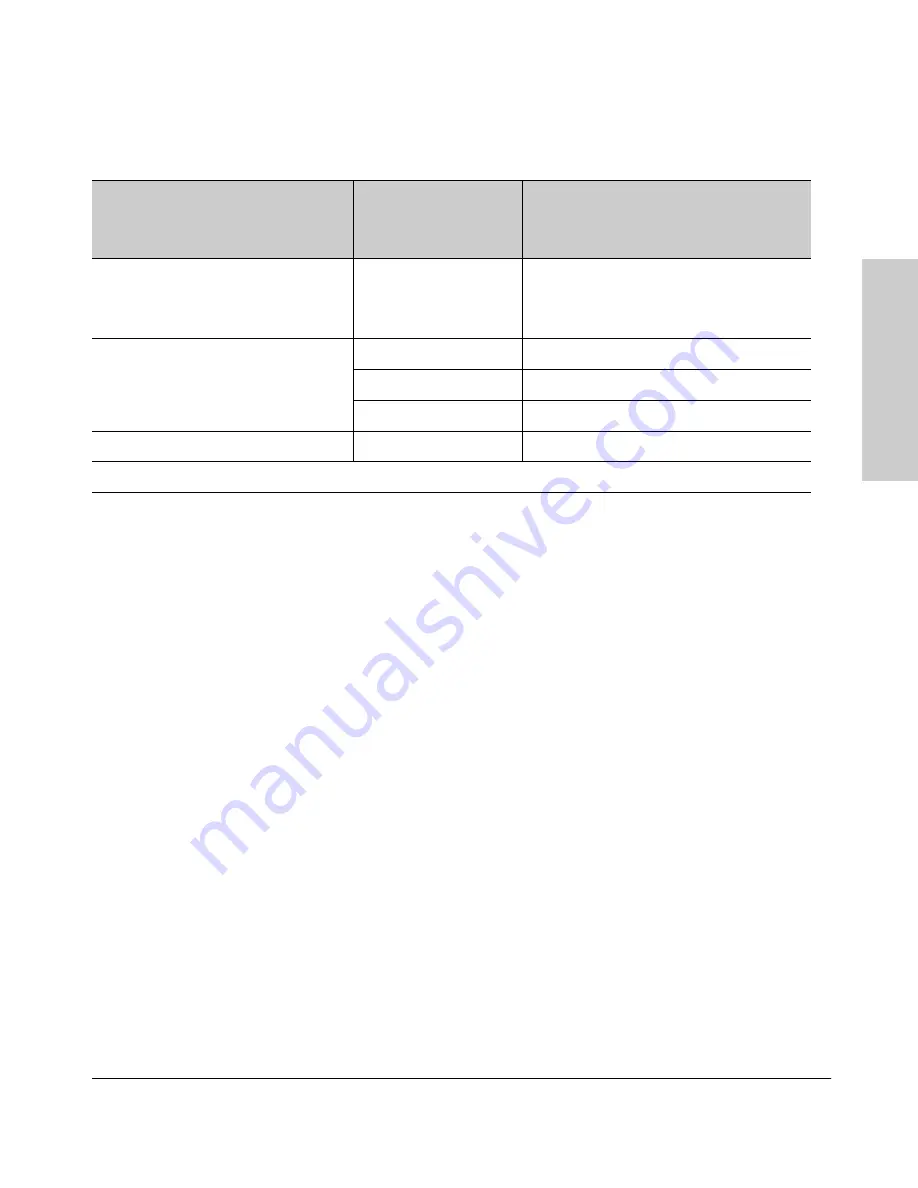
Table 9-3. Stacking Configuration Guide
The easiest way to
automatically
create a stack is to:
1.
Configure a switch as a Commander.
2.
Configure IP addressing and a stack name on the Commander.
3.
Set the Commander’s
Auto Grab
parameter to
Yes
.
4.
Connect Candidate switches (in their factory default configuration) to
the network.
This approach automatically creates a stack of up to 16 switches (including
the Commander). However this replaces manual control with an automatic
process that may bring switches into the stack that you did not intend to
include. With the Commander’s
Auto Grab
parameter set to
Yes
,
any switch
conforming to all four of the following factors automatically becomes a stack
Member:
■
Default stacking configuration (
Stack State
set to
Candidate
, and
Auto Join
set to
Yes
)
■
Same subnet (broadcast domain) and default VLAN as the
Commander (If VLANs are used in the stack environment, see
“Stacking Operation with a Tagged VLAN” on page 9-44.)
■
No Manager password
■
14 or fewer stack members at the moment
Join Method
1
Commander
(IP Addressing Required)
Candidate
(IP Addressing Optional)
Auto Grab
Auto Join
Passwords
Automatically add Candidate to Stack
(Causes the first 15 eligible, discovered
switches in the subnet to automatically
join a stack.)
Yes
Yes
(default)
No
(default)
*
Manually add Candidate to Stack
(Prevent automatic joining of switches
you don’t want in the stack)
No
(default)
Yes
(default)
Optional
*
Yes
No
Optional
*
Yes
Yes
(default)
or
No
Configured
Prevent a switch from being a Candidate N/A
Disabled
Optional
*
The Commander’s Manager and Operator passwords propagate to the candidate when it joins the stack.






























