Functions
6-95
7SJ63 Manual
C53000-G1140-C120-1
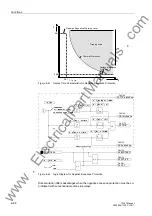
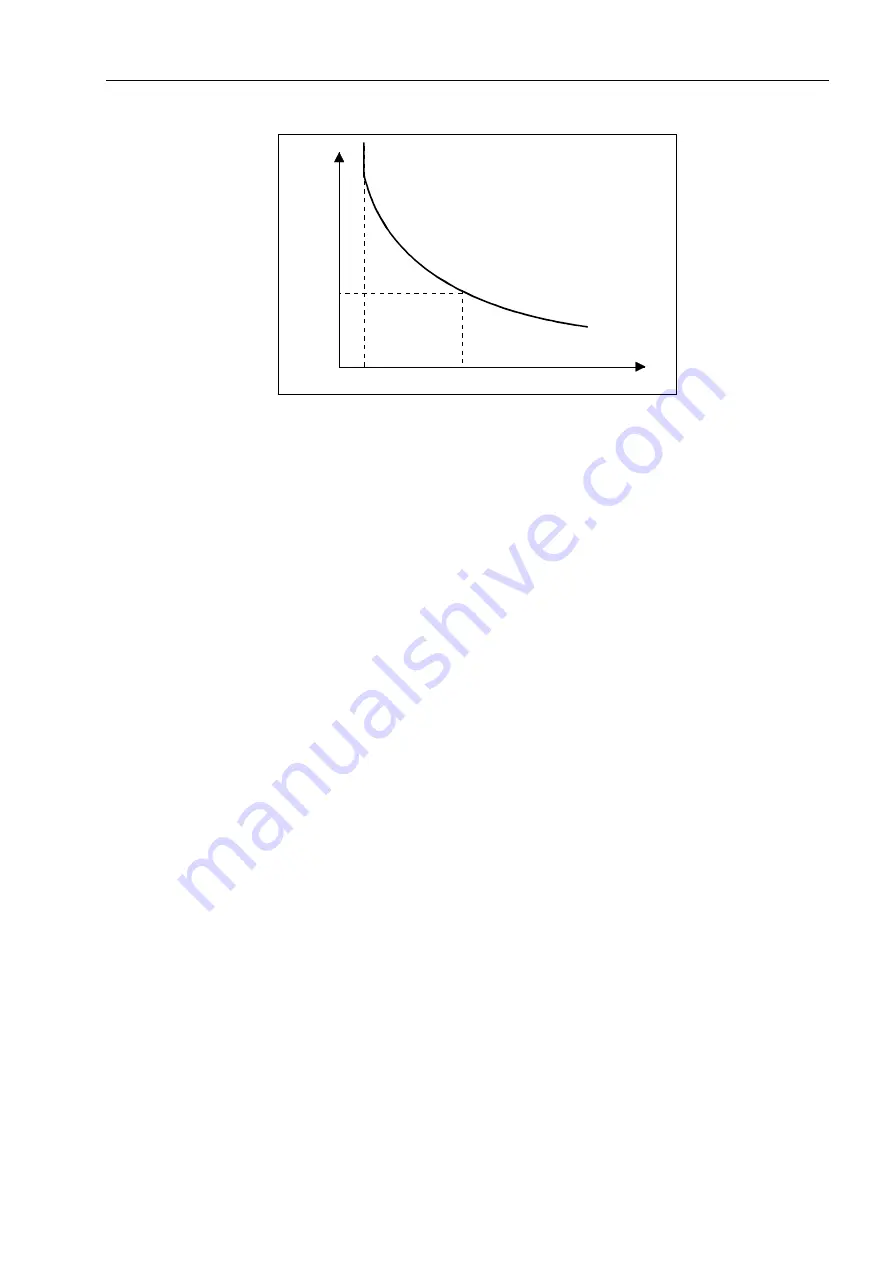
Figure 6-43
Inverse Time Characteristic Tripping Curve for Motor Starting Current
Therefore, if the starting current I actually measured is smaller (or larger) than the
nominal starting current I
A
entered at address
67$5783&855(17
, the actual
tripping time t
trip
is lengthened (or shortened) accordingly. See Figure 6-43.
Definite Time
Time-Overcurrent
Tripping
Characteristic
(Blocked Rotor
Time)
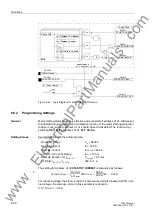
During motor starting, the definite time characteristic is designed to initiate a trip if the
motor starting time exceeds the maximum allowable blocked rotor time. The device
can detect a blocked rotor condition via a binary input from an external rpm-counter.
If the current in any of the phases exceeds the motor starting recognition setting en-
tered at address
, and if a blocked rotor conditions is detected via a binary input,
a motor starting condition is assumed, and time delayed tripping via the definite time
characteristic will be initiated (based on the maximum allowable blocked rotor time).
It is important to note that message generation does not occur unless a trip is initiated.
Furthermore, when a blocked rotor condition is detected via a binary input, and the
definite time characteristic times out, immediate tripping will take place regardless of
whether the blocked rotor condition was detected before or after the definite time char-
acteristic timed out.
Motor starting protection may be switched on or off at address
)&7
. In
addition, motor starting protection may be blocked via a binary input, at which time
pickup messages and time delays will be reset. Figure 6-44 illustrates the logic for mo-
tor starting protection.
I
t
Aus
[s]
I
A
t
Amax
I
MOT ANL
t
TRIP
t
MOT START
www
. ElectricalPartManuals
. com