Functions
6-73
7SJ63 Manual
C53000-G1140-C120-1
6.6
Sensitive Ground Fault Detection (64, 50Ns, 67Ns)
General
Sensitive ground fault detection may be used in isolated or compensated systems to
detect ground faults. In solidly or low-resistance grounded systems, sensitive ground
fault detection is used to detect high impedance ground faults. Sensitive ground fault
detection may be used for alarming and annunciation, or may be allowed to initiate
tripping. Programmable timers are supplied to supervise the alarming and tripping.
Because of its high sensitivity, ground fault detection is not suited for detection of high
magnitude ground faults (over about 1.6 A at the sensitive ground fault detection relay
terminals). The directional and non-directional overcurrent protection functions are
preferred for this application (Sections 6.2 and 6.3).
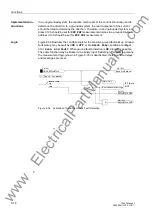
6.6.1
Description of Sensitive Ground Fault Detection
6.6.1.1
Voltage Element
The voltage element of sensitive ground fault detection relies on the zero sequence or
displacement voltage V
0
or 3V
0
. Additionally the faulty phase is determined. The dis-
placement voltage V
0
can be directly applied to the device, or the summary voltage
3V
0
can be calculated by the device based on the three phase-to-ground voltages. In
the latter case, the three voltage inputs must be connected to voltage transformers in
a grounded-wye configuration (see Subsection 6.1.1, address
97&RQQHF
WLRQ
).
If the displacement voltage is directly applied to the device, then V
0
is the voltage at
the device terminals. It is not affected by the voltage adjustment factor set at address
9SK9GHOWD
.
If the displacement voltage is calculated, then:
3V
0
= V
a
+ V
b
+ V
c
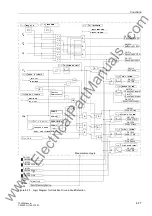
The displacement voltage is used both to detect a ground fault and to determine direc-
tion, in accordance with Subsection 6.6.1.3. When the voltage element pickups, a pre-
set time delay must elapse before detection of the displacement voltage is reported.
This time delay is preset at the factory to 1 second and may be modified at address
7'(/$<3LFNXS
. After the time delay set at address
has elapsed, a sec-
ond time interval may be started, after which the voltage element may initiate a trip sig-
nal. This second time interval is set at address
'(/$<
. It is important to
reiterate that the total tripping time consists of the displacement voltage measurement
time (about 60 ms) plus the Pickup Time delay (set at address
) plus the tripping
delay (set at address
).
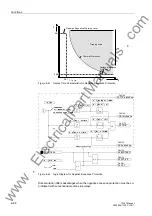
Determination of
the Grounded
Phase
After the voltage element pickups due to detection of a displacement voltage, the
grounded phase is identified, if possible. To do this, the individual phase-to-ground
voltages are measured. Of course, this is only possible if three phase-to-ground volt-
ages are obtained from voltage transformers connected in a grounded-wye configura-
tion. If the voltage magnitude for any given phase is below the setting value entered
at address
93+0,1
, that phase is detected as the grounded phase as long as
www
. ElectricalPartManuals
. com