29
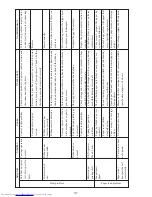
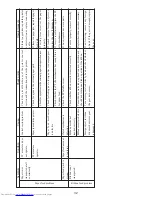
Check points
Countermeasure
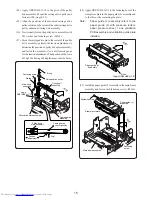
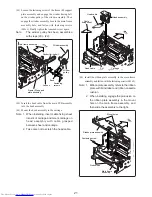
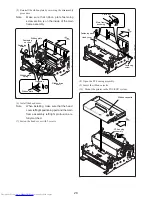
Apply rated voltage (24 V DC) to motor lead solder
points on main PCB assembly (+: red, -: black) and
check whether motor turns.
Measure voltage between pins 10 (+) and 2 (-) of
connector on main PCB assembly and verify that 24 V
DC is supplied.
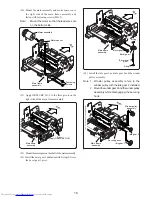
Check conductivity between pin 10 of connector on
main PCB assembly and red motor lead, and pin 2 and
black motor lead.
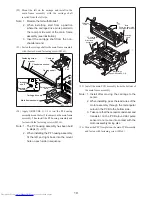
Open PF housing and check for jammed paper or foreign
objects.
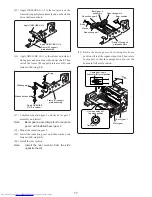
Check whether head wire is tangled in ink ribbon or
paper.
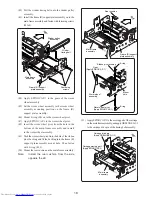
Rotate motor gear by hand and check whether gear train
moves.
If not rotating, replace motor.
If not supplied, repair printer control
section.
If there is no conductivity, replace
main PCB assembly.
Remove any jammed paper or foreign
objects.
Replace print head assembly and
ribbon cassette.
If not moving, remove any foreign
objects or replaced damaged gear.
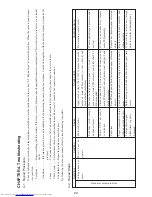
Symptom
Condition
Cause
Carriage does not
move.
Motor does not
operate.
Motor is defective
Problem with voltage
applied to motor
Main PCB assembly
is defective
Paper jam
Paper is jammed with ink
ribbon or print head wire.
Foreign object in gear
wheel train, or gear is
damaged.
Head movement problem
4-1
Repair Procedure
When a problem has occurred, check the symptoms carefully and use the instruction in the section "4-2 Repair Steps" to isolate
the problem. When the cause is found, repair
it as specified.
Symptom
.............
Begin searching with this column. If there are several symptoms, take all applicable items into considerati
on. This will allow you to discover a potential
faults.
Condition
............
Information given here is a precondition for determining the cause in the next column. Use the item togeth
er with the previous column to pinpoint the
problem.
Cause
...................
Lists conceivable causes. Select a possible cause from the list, and verify as described in the next co
lumn.
Check points
.......
Perform these checks to confirm that the problem is really caused by the respective condition.
Countermeasure
..
Repair the problem as described here.
By following the above procedure, effective troubleshooting is possible.
CHAPTER 4. Troubleshooting
4-2
Repair Steps