IV
Part Descriptions
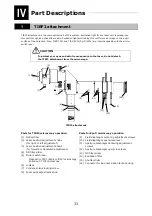
1 TIRF2 attachment
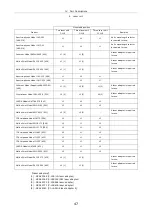
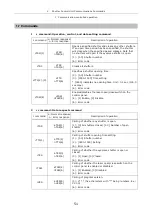
37
(11), (12) Aperture diaphragm
(Aperture diaphragm centering adjustment screws,
Aperture diaphragm open/close lever)
The aperture diaphragm is adjusted by using the aperture diaphragm centering adjustment
screws and the aperture diaphragm open/close lever.
The aperture diaphragm is used to adjust the numerical aperture of an illumination optical
system. When using an episcopic-fluorescent illumination optical system, the aperture
diaphragm functions to adjust the brightness of the image and the size of the stray light.
Although the amount of stray light decreases when the aperture diaphragm is stopped
down, the image of the specimen also becomes darker. Although the image becomes
brighter when the aperture diaphragm is opened, the amount of stray light may also
increase. It is possible to effectively eliminate stray light and secure a bright specimen
image by stopping down the aperture diaphragm to a size equivalent to the diameter of
the objective pupil.
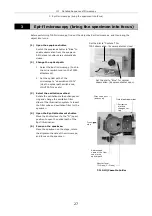
Centering the aperture diaphragm
1
Perform steps [1] to [5] in “3. Epi-fl microscopy” of
chapter “III. Detailed Sequence of Microscopy.”
2
Stop down the aperture diaphragm. (Move the
aperture diaphragm open/close lever to the “C”
(close) direction.)
3
Move the center of the aperture diaphragm image to
the center of the centering tool window. (Turn the
aperture diaphragm centering screws.)
4
Adjust the aperture diaphragm to roughly the size of
the centering tool window. (Adjust the aperture
diaphragm open/close lever.)
5
Once again, move the center of the aperture
diaphragm image to the center of the centering
tool window. (Turn the aperture diaphragm
centering screws.)
(13)
ND filter slider
Once pressed in, the ND filter is placed in the optical path.
ND2, ND8, and ND16 of the TIRF side and ND4 and ND8 of the Epi side can be placed in or
removed from the optical path.
(14)
Excitation filter slider
Up to 3 filters with a maximum thickness
of 5.5mm and a diameter of 25mm can be
attached and used interchangeably with the excitation filter slider.
When the excitation filter is positioned on the slider, not on the filter cube, TIRF
microscopy can be performed without letting a laser beam pass through the excitation
filter.
When using the excitation filter slider with a excitation filter for the
microscopy, always check the barrier filter setting.
If the combination of the excitation filter and the barrier filter is not
correct, strong light may pass through. Be extremaly careful.
Centering tool window
Aperture diaphragm
centering screws
Aperture diaphragm
open/close lever
Aperture diaphragm image
CAUTION
Summary of Contents for TIRF2
Page 1: ...TIRF2 SYSTEM FOR TE2000 INSTRUCTIONS M339E 04 12 NF 2 ...
Page 2: ......