IV
Part Descriptions
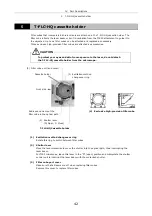
5 T-FLC-HQ cassette holder
44
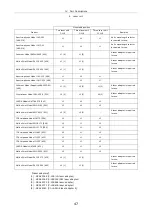
When self-fluorescence is pronounced, use an excitation filter with a narrow bandwidth.
(The resulting fluorescent image will be darker, however.) Excitation filters are likely to
deteriorate the more they are used, since they are exposed to intense light. Replace
excitation filters as necessary.
Narrow
Excitation filter bandwidth
Wide
Brightness of
fluorescent image
Dark Bright
Occurrence of
self-fluorescence
Minimal
Pronounced
Pronounced
Extent of fading
Minimal
Pronounced
Pronounced
2 Selecting barrier filters (BA filters)
A barrier filter allows only fluorescent light generated by the specimen to pass and blocks
all other excitation light reflected from the specimen. This filter makes it possible to
observe the fluorescent image without unnecessary light (i.e., on a dark background).
There are two types of barrier filters: LP filters (long-pass filters), which block all
wavelengths that are shorter than a certain boundary wavelength and allow to pass all
wavelengths that are longer than the boundary wavelength, and BP filters (band-pass
filters), which allow only light in a certain range of wavelengths to pass. Use whichever
type best suits your purposes.
LP filters (long-pass filters)
LP filters block all wavelengths that are shorter than a certain boundary wavelength and
allow to pass all wavelengths that are longer than the boundary wavelength. The boundary
wavelength is called the cut-on wavelength.
(1) When the specimen is stained with a fluorescent color for which the fluorescent light
wavelength band and the excitation wavelength band (the light that is absorbed by the
specimen in order to fluoresce) are extremely close together, the fluorescent light can
generally be seen most effectively if a barrier filter with a “cut-on” wavelength that is
comparatively short, within the range permitted by performance considerations, is
selected.
As a general rule, the longer the cut-on wavelength is, the more complete the
separation between the excitation light and fluorescent light, and the darker the
background of the fluorescent image becomes. Recently, however, because of
improved filter performance, it is becoming increasingly common to use barrier filters
with shorter cut-on wavelengths.
(2) To view the fluorescent images of all the colors in a specimen stained in multiple
colors, use an LP filter.
However, when using a normal dichroic mirror, an
excitation filter, and an LP filter-type barrier filter in
combination, the stain that fluoresces at the longer
wavelength (for example, TRITC when the specimen is
stained with FITC and TRITC) may not be excited
sufficiently, with the result that the fluorescent image
created by the stain may appear extremely dark. In this
type of situation, the use of a multi-band filter is
recommended.
Both the FITC fluorescent image
and the TRITC fluorescent image
are visible.
FITC fluorescent
wavelength band
LP520
TRITC fluorescent
wavelength band
Summary of Contents for TIRF2
Page 1: ...TIRF2 SYSTEM FOR TE2000 INSTRUCTIONS M339E 04 12 NF 2 ...
Page 2: ......