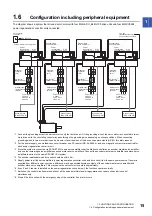
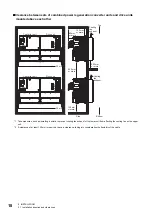
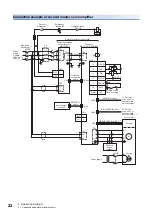
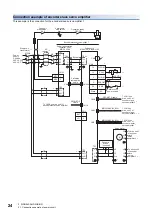
3 SIGNALS AND WIRING
3.1 Connection example of power circuit
23
3
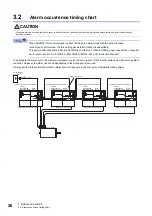
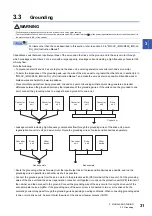
*1 To prevent an unexpected restart of the drive unit, configure a circuit to turn off EM2 (Forced stop 2) in the drive unit when the main
circuit power is turned off.
*2 Always match the phases of the power supply connected to L11 and L21 on the power regeneration converter unit and the drive unit with
the phases connected to L1 and L2. Otherwise, the drive unit and the power regeneration converter unit may malfunction.
*3 Always supply power to the cooling fan terminal. For specifications of the cooling fan power supply and how to detect a failure, refer to
"Servo Motor Instruction Manual (Vol. 3)".
*4 Connect the grounding wire from the servo motor to the protective earth (PE) terminal of the drive unit. Put the grounding wires of the
drive unit and the power regeneration converter unit together
into one on the protective earth (PE) terminal of the cabinet, and then connect to the ground. Connect the grounding wire of the servo
motor to only the drive unit of the encoder master servo amplifier. If the grounding wire of the servo motor is connected to two or more
drive units, the circulating current may pass through the grounding wire depending on wiring conditions. When connecting grounding
wires to two or more drive units, be sure to twist the wires of the drive unit power outputs (U/V/W).
*5 Use a magnetic contactor with an operation delay time (interval between current being applied to the coil until closure of contacts) of 80
ms or less.
*6 For absolute position detection systems, connect an optional battery to only the drive unit of the encoder master servo amplifier. Do not
connect the optional battery to the drive units of the encoder slave servo amplifiers.
*7 Use an external dynamic brake (option) together. Failure to do so will cause an accident, such as machine collision because the servo
motor does not stop immediately but coasts at emergency stop. For wiring of the dynamic brake, refer to the following.
Page 69 External dynamic brake
*8 Encoder signals are distributed to all the drive units in the system via each drive unit.
*9 This diagram shows sink I/O interface. For source I/O interface, refer to section 3.8.3 in MR-J4-_B_(-RJ) Servo Amplifier Instruction
Manual.
*10 Configure a sequence that will shut off the main circuit power when an alarm occurs.
*11 Configure a circuit to simultaneously turn on or off EM2 (Forced stop 2) in the drive units of the encoder master servo amplifier and
encoder slave servo amplifiers.
*12 When not using the STO function, always attach the short-circuit connector supplied with the drive unit.
*13 If the wire size used for the branch circuit is smaller than that used for L1, L2, and L3, install an overcurrent protection device (molded-
case circuit breaker, fuse, or others) to protect the circuit.
*14 Even if an AC reactor is installed on the power regeneration converter unit, the functions operate normally.
*15 A step-down transformer is required when the coil voltage of the magnetic contactor is 200 V class.
*16 Supply power to all the servo amplifiers (power regeneration converter units and drive units) from the same power source. If power is
supplied from different power sources, a difference may be generated between outputs of the encoder master servo amplifier and that of
encoder slave servo amplifiers. This may cause the servo motor to operate unpredictably.
*17 Switch on the control circuit power supplies of all the servo amplifiers (power regeneration converter units and drive units)
simultaneously.
*18 The dynamic brake must be controlled by the drive unit of the encoder master servo amplifier. Assign DB (Dynamic brake interlock) in
[Pr. PD07] to [Pr. PD09].
*19 The encoder cable has a thermistor signal wire. Wiring the thermistor signal is unnecessary.
Summary of Contents for Melservo-J4 MR-J4-DU*B4-RJ100 Series
Page 2: ......
Page 75: ...9 USING STO FUNCTION 73 9 MEMO ...
Page 81: ...11 APPENDIX 11 1 Analog monitor 79 11 MEMO ...
Page 85: ......