10-184
KDFX Reference
KDFX Algorithm Specifications
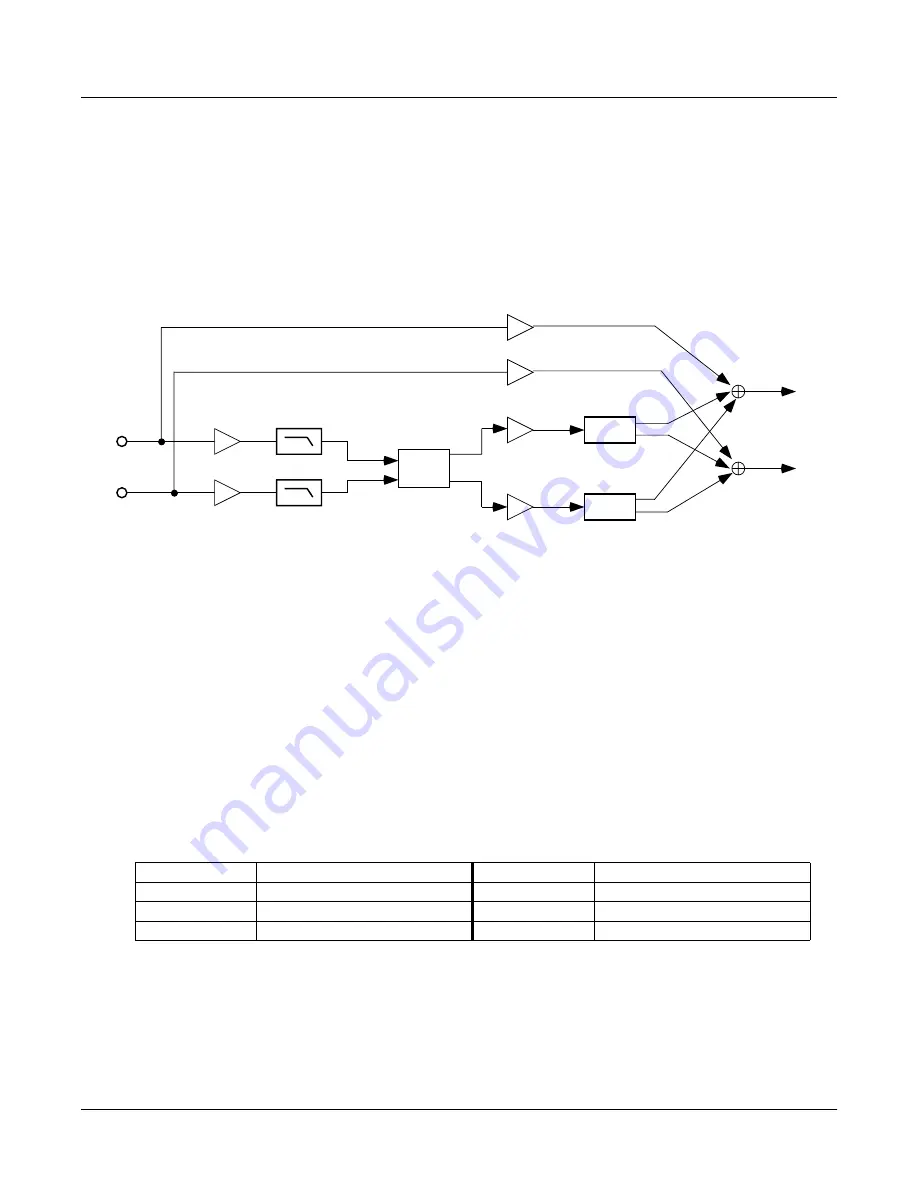
MutualFreqOffset
modulates the two input signals (left and right) with each other. If one of the signals is
a sine wave, the algorithm behaves like
Frequency Offset
. Now imagine that one of the input signals is the
sum of two sine waves. Both of the two sine waves will modulate the signal on the other input. For
example, if the two sine waves are at 100 Hz and 200 Hz, upward modulation of another signal at 1000 Hz
will produce pitches at 1100 Hz and 1200 Hz. Obviously this is going to get very complicated to work out
when the inputs are more than simple sine waves.
MutualFreqOffset
may require extra gain
compensation so separate left, right input gain controls and a gain control for the
fi
nal (wet) output are
provided.
Figure 96
Block diagram of MutualFreqOffset
With downward modulation, you will hear the pitch drop as you increase the frequency of the input
sound. The downward modulation is a difference (subtraction) in frequencies. If the difference drops to
negative values, the frequency will start to rise again. It doesn’t matter which frequency gets subtracted
from the other, since the result will sound the same. For example 1000 Hz - 100 Hz = 900 Hz will produce
the same pitch as 100 Hz - 1000 Hz = -900 Hz. Similarly, upward modulation is a sum of frequencies and
pitch will rise as you increase the frequency of input sound. However in a digital sampled system,
frequencies higher than half the sample rate (the Nyquist rate, 24 kHz in KDFX) cannot be represented.
When the summed frequencies pass the Nyquist rate, the pitch starts coming back down.
Both
Frequency Offset
and
MutualFreqOffset
provide panning with width of the dry input signals
directly to the output.
Parameters (Frequency Offset):
Page 1
Wet/Dry
0 to 100 %wet
Out Gain
Off, -79.0 to 24.0 dB
In Lowpass
8 to 25088 Hz
SSB
Modulator
Pan
Pan
Dry
Wet/Wet Gain
Up
Down
In Gain L
In Gain R
L Input
R Input
L Output
R Output
Low Pass
Summary of Contents for K2661
Page 18: ...2 4 LFOs LFO Shapes...
Page 34: ...3 16 DSP Algorithms...
Page 54: ...5 4 MIDI Note Numbers Note Numbers for Percussion Keymaps...
Page 72: ...7 10 System Exclusive Protocol K2661 System Exclusive Implementation...
Page 82: ...9 4 Upgrading Sample Memory Choosing and Installing a SIMM for K2661 Sample Memory...
Page 334: ...10 252 KDFX Reference KDFX Algorithm Specifications...
Page 340: ...11 6 Glossary...
Page 382: ...12 42 Triple Modular Processing Alphanumeric Buttonpad Entries for DSP Functions...
Page 392: ...B 6 SysEx Control of KDFX MSB and LSB...
Page 442: ...D 20 Contemporary ROM Block Objects Controller Assignments Contemporary ROM Block...
Page 490: ...H 12 General MIDI Standard Mode Controller Assignments...
Page 492: ...I 2 Live Mode Objects Live Mode Programs...
Page 498: ...K2661 Musician s Reference Index...
Page 500: ......
















































