KDFX Reference
KDFX Algorithm Specifications
10-175
914 Revrse LaserVerb
A bizarre reverb which runs backwards in time.
PAUs:
4
Revrse LaserVerb
is a mono effect that simulates the effect of running the
LaserVerb
in reverse. When you
play a sound through the algorithm, it starts out relatively diffuse then builds to the
fi
nal “hit.” Since
KDFX cannot break the universal rules of causality (sorry, KDFX doesn’t know what you are about to
play!), there can be a signi
fi
cant delay between what you play and when you hear it. In addition to the
normal Wet/Dry control, with the Rvrs W/D, the dry signal is considered to be the delayed “hit” signal.
Revrse LaserVerb
is
LaserVerb
in reverse, so when it is fed an impulsive sound such as a snare drum, it
plays the impulse back as a delayed train of closely spaced impulses, and as time passes, the spacing
between the impulses gets closer until they coalesce at the “hit.” The close spacing of the impulses
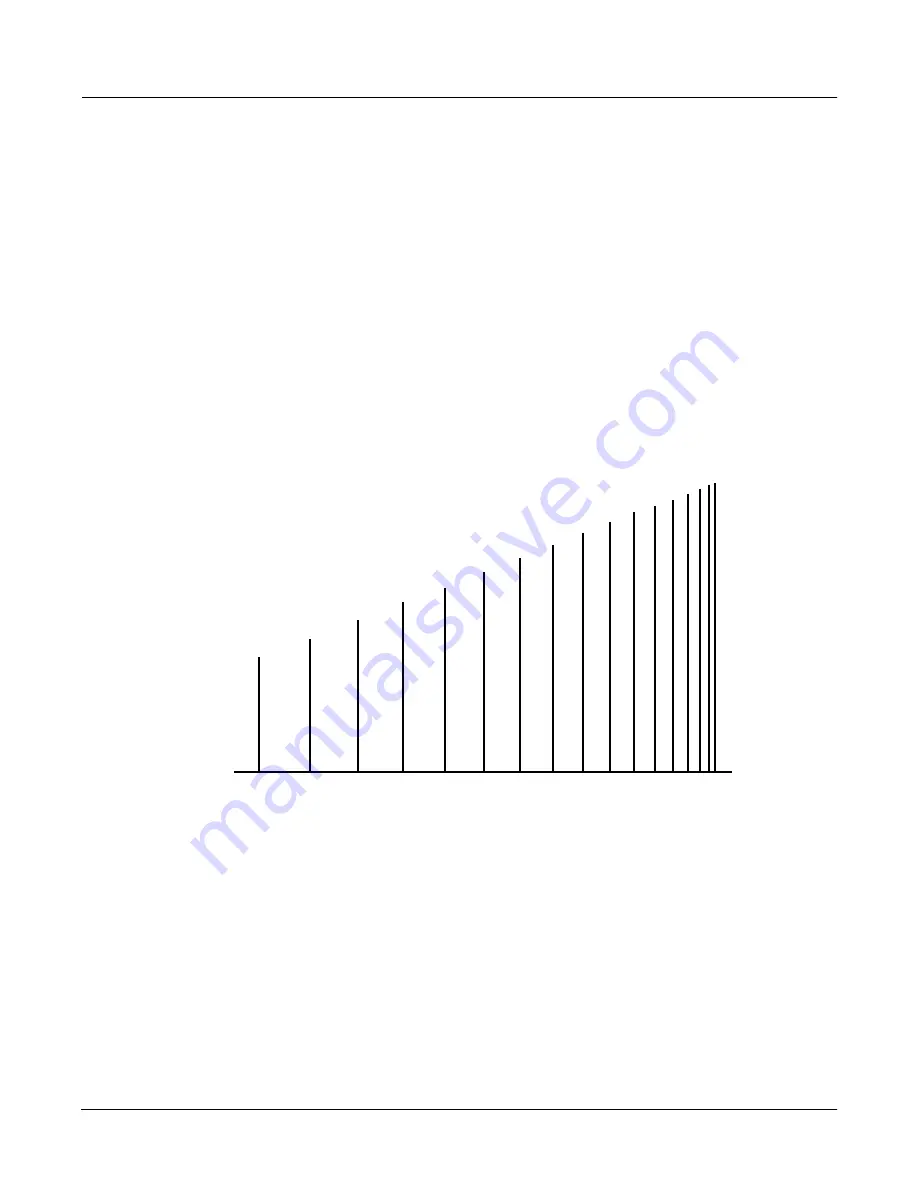
produces a discernible buzzy pitch which gets higher as the impulse spacing decreases. The following
fi
gure is a simpli
fi
ed representation of the
Revrse LaserVerb
impulse response. (An impulse response of a
system is what you would see if you had an oscilloscope on the system output and you gave the system an
impulse or a spike for an input.)
Figure 91
Simplified impulse response of Revrse LaserVerb
With appropriate parameter settings this effect produces an ascending buzz or whine. The ascending buzz
is most prominent when given an impulsive input such as a drum hit. To get the ascending buzz, start with
about half a second of delay and set the Contour parameter to a high value (near
100%
). The Contour
parameter controls the overall shape of the
LaserVerb
impulse response. At high values the response
builds up slowly to the “hit.” As the Contour value is reduced, the response starts out lower and rises
more rapidly to the “hit.”
The Spacing parameter controls the initial separation of impulses in the impulse response and the rate of
their subsequent separation. Low values result in a high initial pitch (impulses are more closely spaced)
and takes longer for the pitch to lower.
t= 0
" hit"
Summary of Contents for K2661
Page 18: ...2 4 LFOs LFO Shapes...
Page 34: ...3 16 DSP Algorithms...
Page 54: ...5 4 MIDI Note Numbers Note Numbers for Percussion Keymaps...
Page 72: ...7 10 System Exclusive Protocol K2661 System Exclusive Implementation...
Page 82: ...9 4 Upgrading Sample Memory Choosing and Installing a SIMM for K2661 Sample Memory...
Page 334: ...10 252 KDFX Reference KDFX Algorithm Specifications...
Page 340: ...11 6 Glossary...
Page 382: ...12 42 Triple Modular Processing Alphanumeric Buttonpad Entries for DSP Functions...
Page 392: ...B 6 SysEx Control of KDFX MSB and LSB...
Page 442: ...D 20 Contemporary ROM Block Objects Controller Assignments Contemporary ROM Block...
Page 490: ...H 12 General MIDI Standard Mode Controller Assignments...
Page 492: ...I 2 Live Mode Objects Live Mode Programs...
Page 498: ...K2661 Musician s Reference Index...
Page 500: ......
















































