Rev. 2.10
170
���� 02� 201�
Rev. 2.10
171
���� 02� 201�
HT68F20/HT68F30/HT68F40/HT68F50/HT68F60
HT68FU30/HT68FU40/HT68FU50/HT68FU60
Enhanced I/O Flash Type 8-Bit MCU with EEPROM
HT68F20/HT68F30/HT68F40/HT68F50/HT68F60
HT68FU30/HT68FU40/HT68FU50/HT68FU60
Enhanced I/O Flash Type 8-Bit MCU with EEPROM
SPI Interface
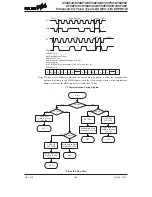
The SPI interface is often used to communicate with external peripheral devices such as sensors,
Flash or EEPROM memory devices etc. Originally developed by Motorola, the four line SPI
interface is a synchronous serial data interface that has a relatively simple communication protocol
simplifying the programming requirements when communicating with external hardware devices.
The communication is full duplex and operates as a slave/master type, where the device can be
either master or slave. Although the SPI interface specification can control multiple slave devices
from a single master, but this device provided only one SCS pin. If the master needs to control
multiple slave devices from a single master, the master can use I/O pin to select the slave devices.
SPI Interface Operation
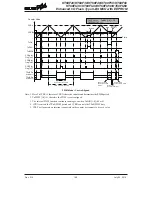
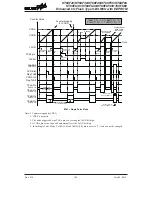
The SPI interface is a full duplex synchronous serial data link. It is a four line interface with pin
names SDI, SDO, SCK and SCS. Pins SDI and SDO are the Serial Data Input and Serial Data
Output lines, SCK is the Serial Clock line and SCS is the Slave Select line. As the SPI interface
pins are pin-shared with normal I/O pins and with the I
2
C function pins, the SPI interface must
first be enabled by selecting the SIM enable configuration option and setting the correct bits in the
SIMC0 and SIMC2 registers. After the SPI configuration option has been configured it can also
be additionally disabled or enabled using the SIMEN bit in the SIMC0 register. Communication
between devices connected to the SPI interface is carried out in a slave/master mode with all data
transfer initiations being implemented by the master. The Master also controls the clock signal.
As the device only contains a single SCS pin only one slave device can be utilized. The SCS pin is
controlled by software, set CSEN bit to "1" to enable SCS pin function, set CSEN bit to "0" the SCS
pin will be floating state.
SPI Master/Slave Connection
The SPI function in this device offers the following features:
• Full duplex synchronous data transfer
• Both Master and Slave modes
• LSB first or MSB first data transmission modes
• Transmission complete flag
• Rising or falling active clock edge
• WCOL and CSEN bit enabled or disable select
The status of the SPI interface pins is determined by a number of factors such as whether the device
is in the master or slave mode and upon the condition of certain control bits such as CSEN and
SIMEN.
There are several configuration options associated with the SPI interface. One of these is to
enable the SIM function which selects the SIM pins rather than normal I/O pins. Note that if the
configuration option does not select the SIM function then the SIMEN bit in the SIMC0 register will
have no effect. Another two SPI configuration options determine if the CSEN and WCOL bits are to
be used.