Rev. 2.10
28
���� 02� 201�
Rev. 2.10
29
���� 02� 201�
HT68F20/HT68F30/HT68F40/HT68F50/HT68F60
HT68FU30/HT68FU40/HT68FU50/HT68FU60
Enhanced I/O Flash Type 8-Bit MCU with EEPROM
HT68F20/HT68F30/HT68F40/HT68F50/HT68F60
HT68FU30/HT68FU40/HT68FU50/HT68FU60
Enhanced I/O Flash Type 8-Bit MCU with EEPROM
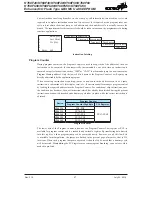
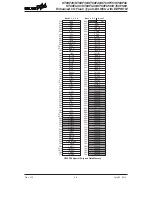
Stack
This is a special part of the memory which is used to save the contents of the Program Counter only.
The stack has multiple levels depending upon the device and is neither part of the data nor part of
the program space, and is neither readable nor writeable. The activated level is indexed by the Stack
Pointer, and is neither readable nor writeable. At a subroutine call or interrupt acknowledge signal, the
contents of the Program Counter are pushed onto the stack. At the end of a subroutine or an interrupt
routine, signaled by a return instruction, RET or RETI, the Program Counter is restored to its previous
value from the stack. After a device reset, the Stack Pointer will point to the top of the stack.
If the stack is full and an enabled interrupt takes place, the interrupt request flag will be recorded but
the acknowledge signal will be inhibited. When the Stack Pointer is decremented, by RET or RETI,
the interrupt will be serviced. This feature prevents stack overflow allowing the programmer to use
the structure more easily. However, when the stack is full, a CALL subroutine instruction can still
be executed which will result in a stack overflow. Precautions should be taken to avoid such cases
which might cause unpredictable program branching.
If the stack is overflow, the first Program Counter save in the stack will be lost.
P r o g r a m C o u n t e r
S t a c k L e v e l 1
S t a c k L e v e l 2
S t a c k L e v e l 3
S t a c k L e v e l N
P r o g r a m
M e m o r y
T o p o f S t a c k
S t a c k
P o i n t e r
B o t t o m o f S t a c k
Device
Stack Levels
HT68F20/HT68F30
�
HT68F�0/HT68F50
8
HT68F60
12
Arithmetic and Logic Unit – ALU
The arithmetic-logic unit or ALU is a critical area of the microcontroller that carries out arithmetic
and logic operations of the instruction set. Connected to the main microcontroller data bus, the ALU
receives related instruction codes and performs the required arithmetic or logical operations after
which the result will be placed in the specified register. As these ALU calculation or operations may
result in carry, borrow or other status changes, the status register will be correspondingly updated to
reflect these changes. The ALU supports the following functions:
• Arithmetic operations: ADD, ADDM, ADC, ADCM, SUB, SUBM, SBC, SBCM, DAA
• Logic operations: AND, OR, XOR, ANDM, ORM, XORM, CPL, CPLA
• Rotation RRA, RR, RRCA, RRC, RLA, RL, RLCA, RLC
• Increment and Decrement INCA, INC, DECA, DEC
• Branch decision, JMP, SZ, SZA, SNZ, SIZ, SDZ, SIZA, SDZA, CALL, RET, RETI