G.Weike Laser
Profession Laser Manufacturer more than 15 Years.
45
Form 5-2 Relationship between focus and
cutting material
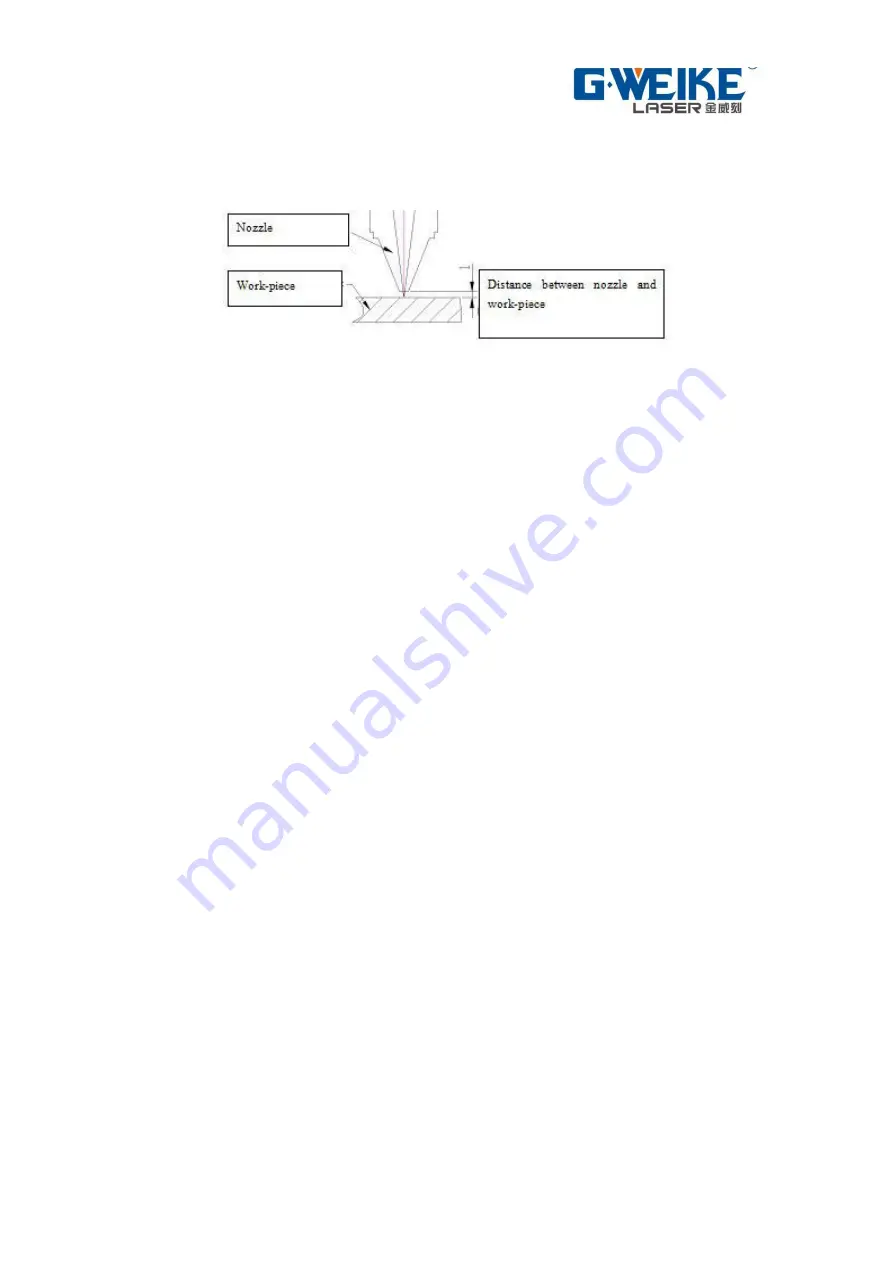
5.6.3 Set distance between nozzle and work piece
Picture 5-24: Distance between nozzle and work
piece
After adjusting sensor adjustment box, the follow-up distance between
nozzle and work piece is adjusted by YRC Cutting head box of teaching.
Please refer to instruction of cutting head.
5.7 Laser cutting process principle
Laser cutting is an advanced and widely applied cutting technology in material
processing. It used high energy density of laser beam as “cuttingtool” for hot
cutting of the material. Adopting laser cutting technology could achieve all kinds
of metal cutting, non-metal cutting and composite materialcutting.
Widely used in every aspect.
5.7.1 Laser cutting principle
Laser cutting is the use of the focus’ high power, high density of laser beam
artifacts, cause the place material rapidly melting, gratification, ablation, or reach
the ignition point, at the same time with the aid of high-speed airflow and beam
coaxial purify molten material, so as to realize start cutting, laser cutting is one of
the hot cutting method.
5.7.1.1 Main mode of laser cutting
Laser fusion cutting and laser oxygen cutting
Laser fusion cutting
Laser fusion cutting is with laser heating melt metal materials, and then through
the nozzle with beam coaxial injection of oxidizing gas (N
2
, Ar, He, etc.) rely on
the strong pressure of the gas to liquid metal, forming slot. Laser fusion cutting
does not need to make the metal completely vaporized; the laser energy
required is only about ten molecule vaporizing cutting, about10
7
W/cm
2.
1).Laser beam to the surface, in addition to the reflection loss, the remaining
energy is absorbed and heated evaporation materials into holes;
2).Once the holes forming, it as a black body to absorb all the beam energy,
small hole is surrounded by a wall of molten metal, relying on the high speed air
flow, melt wall remained relatively stable;
3).Melt isotherm artifacts rely on the secondary air injection pressure, made melt
materials blow away;
















































