l
BrFull6W()
l
BrHalf4W()
l
TCDiff()
For more information on voltage measurements, see
Improving voltage measurement quality
137) and
Analog measurement specifications
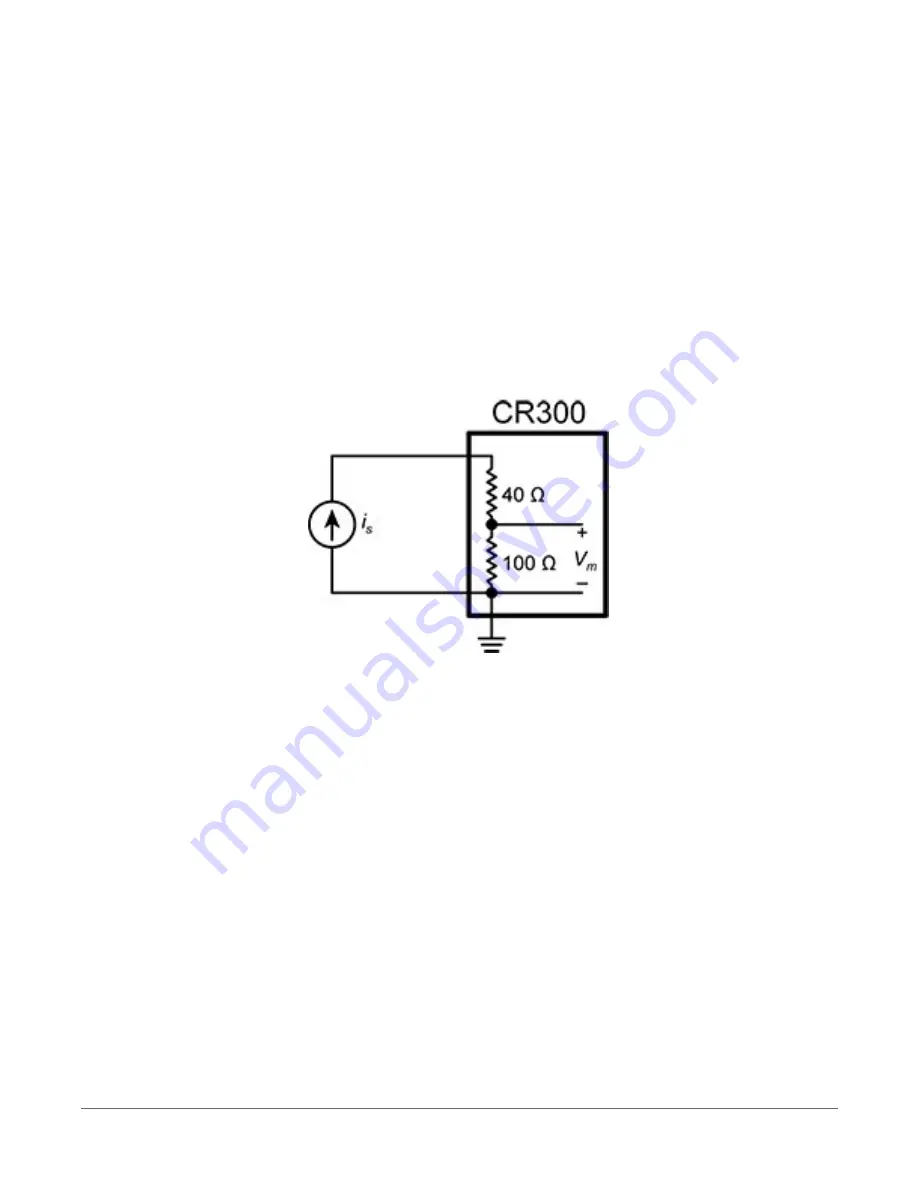
14.2 Current-loop measurements
Terminals SE1 and SE2 can be configured to make analog current measurements using the
CurrentSE()
instruction. Current is measured across the 100 Ω resistor with 140 Ω total
resistance to ground. The following image shows a simplified schematic of a current
measurement.
Use a CURS100 terminal input module when an application needs more than 2 current inputs or
measurements. For detailed instructions, see
http://www.campbellsci.com/curs100
14.2.1 Voltage Ranges for Current Measurements
The data logger measures the current through the use of a 100 Ω resistor. Thus, like a single-
ended voltage instruction, it requires a voltage range option. In general, use the smallest fixed-
input range that accommodates the full-scale output of the transmitter. This results in the best
measurement accuracy and resolution.
To select the appropriate voltage range, the expected current output range must be known.
Using Ohm’s Law, multiply the maximum expected current by 100 Ω to find the maximum voltage
to be measured. Because the maximum voltage input is 2500 mV, the maximum current input
must be 25 mA or less.
14. Measurements
70






























