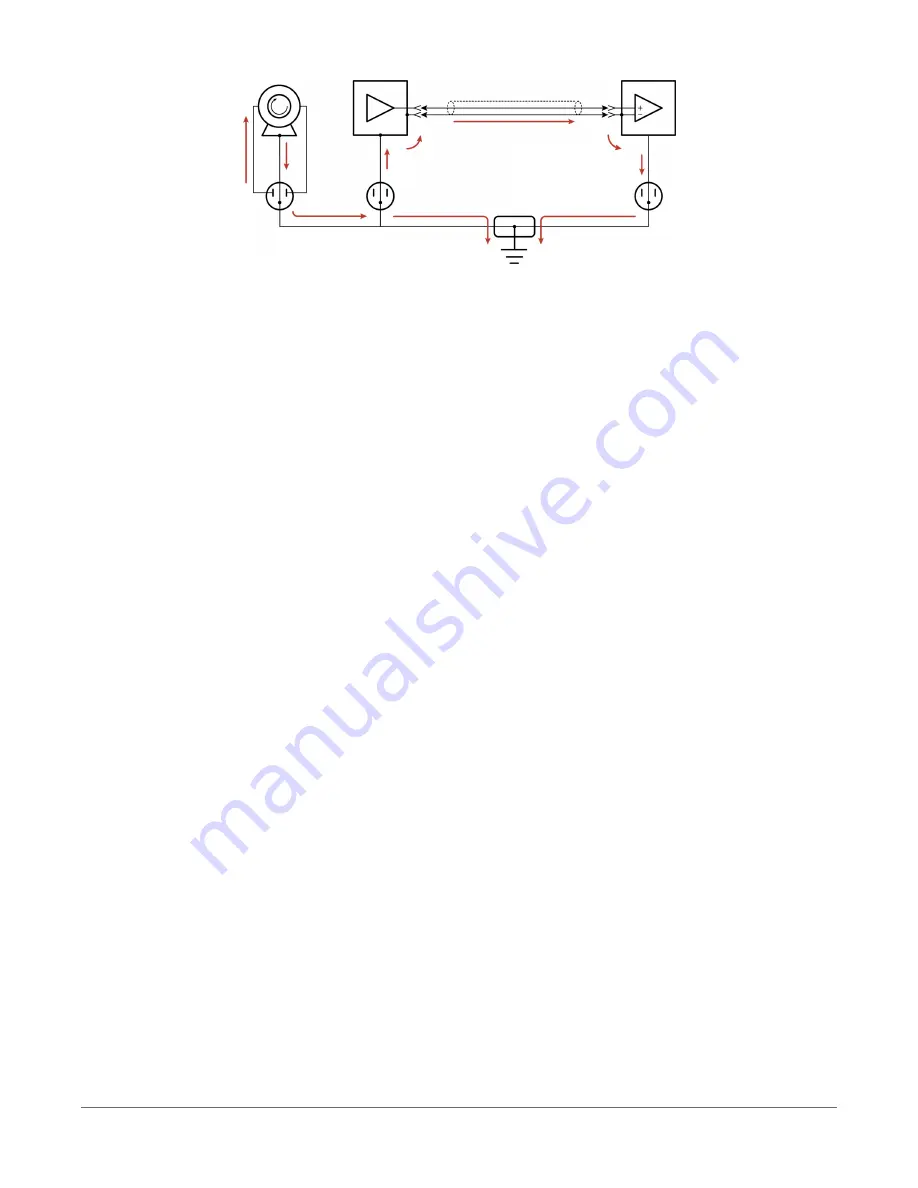
FIGURE 17-2. Leakage current (AC or DC) from nearby load
l
One effect of this DC ground current-flow is a voltage offset error in analog measurements.
Errors of this sort are usually not obvious but can have meaningful effects on
measurements.
l
For digital communications, an offset in the ground voltage reduces the dynamic range of
the digital signals. This makes them more susceptible to noise corruption. If the ground
voltage changes by one volt or more, the digital communications could stop working
because the signals no longer reach the thresholds for determining the state of each bit.
l
If the ground voltage differences reach several volts, damaging effects may occur at the
terminals of the electronics devices. Damage occurs when the maximum allowable voltage
on the internal components is exceeded.
17.10.3 Severing a ground loop
To avoid or eliminate ground loops, when they are detected, requires severing the loop.
Suggestions for severing ground loops include:
l
Connect the shield wire of a signal cable to ground only at one end of the cable. Leave the
other end floating (not connected to ground).
l
Never intentionally use the shield (or drain wire) of a cable as a signal ground or power
ground.
l
Use the mechanical support structure only as a connection for the safety ground (usually
the ground lug). Do not intentionally return power ground through the structure.
l
Do not use shielded Cat5e cables for Ethernet communications.
l
For long distance communication protocols such as RS-485, RS-422, and CAN, use the RG
terminal for the ground connection. The RG terminal has a 100-ohm resistor in series with
ground to limit the amount of DC current than can flow between the two endpoints while
keeping the common-mode voltage in range of the transceivers. The transceivers
17. Tips and troubleshooting
135
















































