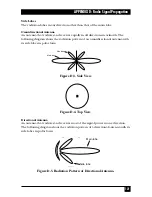
125
APPENDIX E: IEEE 802.11 Technical Tutorial
Appendix E. IEEE 802.11 Technical
Tutorial
The purpose of this chapter is to give you a basic overview of the IEEE 802.11
Standard. You’ll be able to understand the basic concepts, principles of operation,
and reasons behind some of the features of the Standard.
The document does not cover the entire Standard and does not provide enough
information for you to implement an 802.11-compliant device (for this purpose
you should refer to the Standard itself).
E.1 Architecture Components
An 802.11 LAN is based on a cellular architecture where the system is subdivided
into cells. Each cell (called Basic Service Set, or BSS, in the 802.11 nomenclature)
is controlled by a Base Station (called Access Point).
Although a wireless LAN may be formed by a single cell, with a single Access Point
(and, as will be described later, it can also work without an Access Point), most
installations will be formed by several cells, where the Access Points are connected
through some kind of backbone (called Distribution System or DS). This backbone
is typically Ethernet but, in some cases, might be wireless itself.
The whole interconnected wireless LAN, including the different cells, their
respective Access Points and the Distribution System, is seen as a single 802
network to the upper layers of the OSI model and is known in the Standard as the
Extended Service Set (ESS).
The following diagram shows a typical 802.11 LAN including the components
described above:
Summary of Contents for LW0050A
Page 2: ......