122
PRO 11 SERIES WIRELESS ETHERNET
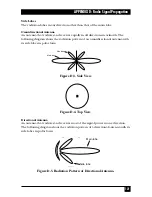
Antenna Beamwidth
The directiveness of a directional antenna. Defined as the angle between two half-
power (-3 dB) points on either side of the main lobe of radiation.
S
YSTEM
C
HARACTERISTICS
Receiver Sensitivity
The minimum RF signal power level required at the input of a receiver for certain
performance.
EIRP (Effective Isotropic Radiated Power)
The power transmitted by an antenna. Equal to the transmitted output power
minus cable loss plus the transmitting antenna gain.
Pout Output power of transmitted in dBm
Ct
Transmitter cable attenuation in dB
Gt
Transmitting antenna gain in dBi
Gr
Receiving antenna gain in dBi
Pl
Path loss in dB
Cr
Receiver cable attenuation in dB
Si
Received power level at receiver input in dBm
Ps
Receiver sensitivity in dBm
Si = Pout - Ct + Gt - Pl + Gr - Cr
EIRP = Pout - Ct + Gt
Example:
Link Parameters:
Frequency: 2.4 GHz
Pout = 4 dBm (2.5 mW)
Tx and Rx cable length (Ct and Cr) = 10 m cable type RG214 (0.6 dB/meter)
Tx and Rx antenna gain (Gt and Gr) = 18 dBi
Distance between sites = 3 km
Receiver sensitivity (Ps) = -84 dBm
Link Budget Calculation:
EIRP = Pout - Ct + Gt = 16 dBm
Pl = 32.4 + 20
×
Log(FMHz) + 20
×
Log(Rkm) @ 110 dB
Si = EIRP - Pl + Gr - Cr = -82 dBm
Summary of Contents for LW0050A
Page 2: ......