120
PRO 11 SERIES WIRELESS ETHERNET
Attenuation is expressed in dB as follows:
PdB = -10
×
Log (Pout/Pin)
For example:
If, because of attenuation, half the power is lost (Pout/Pin =
1/2), then attenuation in dB is -10
×
Log (1/2) = 3 dB
P
ATH
L
OSS
Loss of power of an RF signal traveling (propagating) through space. It is
expressed in dB. Path loss depends on:
• The distance between transmitting and receiving antennas.
• Line-of-sight clearance between the receiving and transmitting antennas.
• Antenna height.
F
REE
-S
PACE
L
OSS
Attenuation of the electromagnetic wave while propagating through space. This
attenuation is calculated using the following formula:
Free-space loss = 32.4 + 20
×
Log(FMHz) + 20
×
Log(Rkm)
F is the RF frequency expressed in MHz.
R is the distance between the transmitting and receiving antennas.
At 2.4 GHz, this formula is: 100+20
×
Log(Rkm)
A
NTENNA
C
HARACTERISTICS
Isotropic Antenna
A hypothetical antenna having equal radiation intensity in all directions. Used as a
zero-dB gain reference in directivity calculation (gain).
Antenna Gain
A measure of directivity. It is defined as the ratio of the radiation intensity in a
given direction to the radiation intensity that would be obtained if the power
accepted by the antenna was radiated equally in all directions (isotopically).
Antenna gain is expressed in dBi.
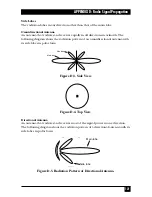
Radiation Pattern
A graphical representation in either polar or rectangular coordinates of the spatial
energy distribution of an antenna.
Summary of Contents for LW0050A
Page 2: ......