26
12.4.2.1. PID REGULATION
The PID algorithm enables achieving smaller control errors (e.g.
temperature) than the ON-OFF method with hysteresis. However, the
algorithm requires selecting the characteristic parameters for the specific
controlled object (e.g. a furnace). In order to simplify the operation, the
controller is provided with the advanced PID parameter selection functions
described in chapter 12.4.2.2. Also, it is always possible to manually correct
the settings (chapter 12.4.2.3).
PID type control is active when the
PID Selection for the SP...
parameter
(both for the setpoint values for the individual outputs, chapter 12.4.1, and
for sections of program control, chapter 12.4.2) indicates one of the
Sets of
PID parameters
(chapter 12.4.2). The location of the
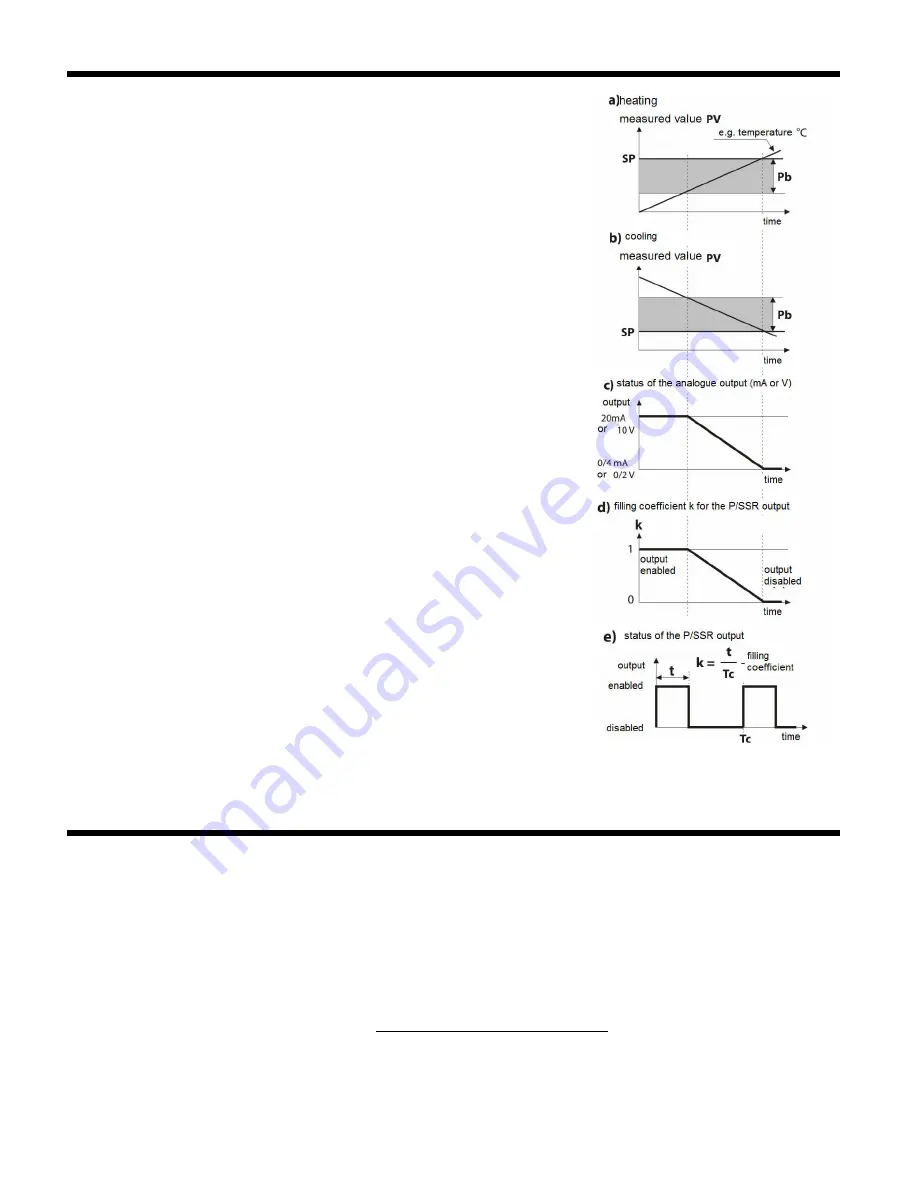
Proportional band Pb
in relation to the setpoint value
SP
is shown in drawings 12.4.2.1 a) and b).
The impact of the integrating and differentiating component of the PID
control is set by the parameters
Integration time constant Ti
and
Differentiation time constant Td
. The parameter
Impulse parameter Tc
applies only to outputs of the P/SSR type. If the PID algorithm is
implemented by the 0/4÷20 mA or 0/2÷10 V analogue output, the
Pulsing
period Tc
parameter is insignificant. Then the output signal may assume
intermediate values from the entire range of variability of the output.
Regardless of the type of the output, the correction of its state always takes
place every 1 s.
The principle of P-type control (proportional control) for the P/SSR output is
shown in figures d) and e) and, that for the analogue output, in figure c).
Fig. 12.4.2.1. Principle of operation of PID control:
a) location of the range of proportionality
Pb
in relation to the setpoint
value
SP
for heating (parameter
Control type
=
Reverse/heating
)
b) location of the range of proportionality
Pb
in relation to the setpoint
value
SP
for cooling (
Control type
=
Direct/cooling
)
c) state of the 0/4÷20 mA or 0/2÷10 V analogue output
d) filling coefficient for the bistate output of the P/SSR type
e) state of the P/SSR output (for the measured value within the
proportionality range
Pb
)
12.4.2.2. AUTOTUNING OF PID PARAMETERS
In order to use the PID parameter selection function for a specific control output, it is firs necessary to select the
Set of PID parameters
(using the parameters
PID selection for SP1
or
SP2
, chapter 12.4.1) for which the calculated
data will be saved, and then to set the autotuning type (using the parameter
Autotuning of PID parameters
). The
autotuning starts at the time of start of the control (automatic or manual, chapter 12.4.1.1). Operation of
autotuning is independent for each of the outputs and is signalized with the message
ST-PID
in the status of the
control channel shown in the window of the
CONTROL
type (chapter 11.2) and in the
Quick configuration screen
(chapter 11.7).
The value of the
Autotuning of PID parameters
determines the selection of the method of selection of PID parameters:
a)
Automatic selection (continuous mode)
- the controller continuously checks if there are appropriate conditions
for starting the tuning and tests the object in order to select the proper method. The algorithm continuously
forces operation in the PID mode. The necessary condition for initiation of the PID parameters selection
procedure is the location of the current measured value
PV
(indicated by the parameter
Assignment of control
signal
) outside of the insensitivity zone defined as the sum of the values of the parameters
Proportional band






























