52 PPC11A 6U VME Single Board Computer
Publication No. PPC11A-HRM/1
4.19
PCIe Infrastructure
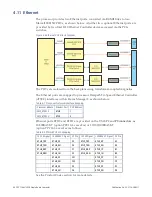
PCI devices and mezzanine sites are connected to the processor using PCIe. The
shows the PCIe and PCI structure of the PPC11A.
PCIe is a high-speed serial, point-to-point interconnect running at 2.5 Gbits/s in each
direction. PCIe links are scalable, meaning that multiple lanes can be used between
devices to increase the aggregate bandwidth. The following table shows a
comparison of the bandwidth of PCIe links with PCI implementations:
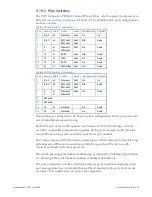
Table 4-23 PCI and PCIe Bandwidths
Bus Type Bus Width Frequency Bandwidth (MB/s) Notes
PCI
32-bit
33 MHz
133
PCI
32-bit
66 MHz
266
PCI
64-bit
66 MHz
533
PCI-X
64-bit
133 MHz
1066
PCIe
x1
2.5 Gbps
250
Per direction
PCIe
x4
2.5 Gbps
1000
Per direction
PCIe
x8
2.5 Gbps
2000
Per direction
PCIe Bandwidths shown include 8b/10b encoding overheads
PCIe is a packet-based protocol, but uses the same address spaces as standard PCI,
meaning that the software interfaces are backwards-compatible. PCIe-to-PCI Bridges
are used to convert to PCI-X or standard PCI where connection to these devices is
required.
The maximum packet payload size for the PCIe sub-system is 256 Bytes.
CRC error-checking is performed on each packet transmitted between devices in the
system, and any corrupted packets are retransmitted. The target device can also
perform end-to-end error-checking, to ensure integrity of the received data.
4.19.1 Processor
The PPC11A supports a x4 link between the host processor and each central PCIe
Switch (see overleaf). The link uses serdes lanes A to D on the host processor to
connect to the first PCIe switch and serdes lanes E to H to connect to the second PCIe
switch. These links operate at Gen2 speed (5 Gbps).