-160-
Glossary
Description
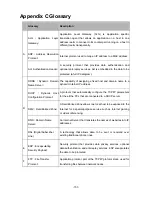
TCP
(
Transfer Control
Protocol
)
Connection-oriented transport layer protocol that provides
reliable full-duplex data transmission.
TCP/IP
(
Transmission
Control Protocol/ Internet
Protocol
)
Common name for the suite of protocols to support the
construction of worldwide Internet works. TCP and IP are the
two best-known protocols in the suite.
T
Telnet
(
Telecommunication
Network protocol
)
Telnet is used for remote terminal connection, enabling users to
log in to remote systems and use resources as if they were
connected to a local system.
UDP
(
User Datagram
Protocol
)
UDP is a simple protocol that exchanges datagram without
acknowledgments or guaranteed delivery, requiring that error
processing and retransmission be handled by other protocols.
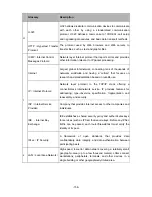
UPnP
(
Universal Plug and
Play
)
UPnP is a set of networking protocols for primarily residential
networks without enterprise class devices that permits
networked devices.
U
URL
(
Uniform Resource
Locator
)
URL describes the access method and the location of an
information resource object on the Internet
VLAN
(
Virtual Local Area
Network
)
Group of devices on one or more LANs that are configured
(using management software) so that they can communicate as
if they were attached to the same wire, when in fact they are
located on a number of different LAN segments. Because
VLANs are based on logical instead of physical connections,
they are extremely flexible.
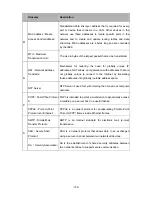
V
VPN
(
Virtual Private
Network
)
Enables IP traffic to travel securely over a public TCP/IP
network by encrypting all traffic from one network to another.
W WAN
(
Wide Area Network
)
Data communications network that serves users across a broad
geographic area and often uses transmission devices provided
by common carriers.