C905
1222-9526 rev. 1
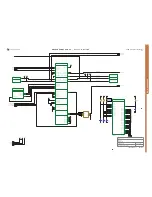
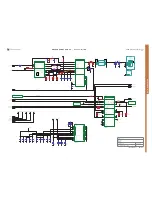
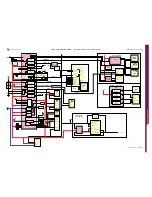
FUNCTIONAL OVERVIEW
FU
N
C
T
IO
N
A
L O
V
E
R
V
IE
W
Technical Description
The functional blocks of the digital baseband controller:
Keypad
The keypad interface block supports up to 30 keys with 65 columns and 6 rows and
operates in both scan and idle mode. The keypad scan is performed by software. Any
transition in the state of the column inputs is written directly to the register. The keypad
interface differentiates between single key presses, simultaneous presses of any keys
with a function key, and any key releases. The period between successive scans is
programmable over the range 5 ms to 80 ms, in 5 ms steps. During scan mode, the
keypad generates an interrupt whenever a valid keypad state change occurs (including a
release of any pressed keys). The scan function is disabled during system power-up. The
keypad is able to detect at least four simultaneous key presses. Not all combinations are
supported.
Radio Part
Antenna
The mobile system antenna interface connects the Wideband Code Division Multiple
Access (WCDMA) and Global System for Mobile Communication (GSM) input/output to
the antenna of the Mobile Phone. It is a bi-directional RF interface containing signals in
the range 800 MHz to 2.2 GHz. The mobile system antenna interface is the interface
between the Mobile Phone Radio Frequency (RF) input/output and the mobile system
antenna. The interface handles the GSM 850, EGSM 900, GSM 1800, GSM 1900 and
WCDMA Band I, II and V, RF inputs/outputs.
Mobile System Antenna Interface:
Radio Module N1200 (Tiger)
Front End
The Front End block connects the proper block in the radio system to the antenna. The
Front End has two inputs for EDGE/GSM/GPRS, one for low band (850/900 MHz) and
one for high band (1800/1900 MHz). The EDGE/GSM/GPRS power amplifier output is
filtered by the low pass filter in the Front End and then connected to the antenna
through a switch. In receive mode, the EDGE/GSM/GPRS signal from the antenna passes
through the switch to one of the four receive SAW filters. The SAW filter provides receive
band selectivity. In GSM/GRPS/EDGE systems, transmit and receive operations are
divided in time and the switch connects the proper block in accordance with the mode of
operation (that is, transmit or receive; one at a time).
In WCDMA the transmit outputs from the WCDMA transceiver are filtered by an external
SAW filter that cleans up the spectrum. The SAW filter output is connected to the power
amplifier, one for each band. For power control, a sample of the transmit output is taken
by a directional coupler and converted to a DC level by the power detection circuit. This
signal is used to control the transmitter output power. The transmit signal passes
through an isolator and then a duplexer. The duplexer output is selected by the switch in
the Front End for connection to the antenna. In WCDMA receive mode the signal from
the antenna is switched by the Front End to the correct duplexer. The output from the
duplexer is connected to the LNA input in the WCDMA receiver.
Transceiver
The transceiver is a multi-mode transceiver for WCDMA/EGDE/GPRS/GSM. The
EDGE/GPRS/GSM part of the transceiver use a digital baseband interface that is shared
between received and transmitted data. The receive interface is based on I and Q data
and the transmitter interface is based on envelope and frequency data. The WCDMA part
of the transceiver use differential analog in-phase and quadrature-phase interfaces,
which is an IQ-interface, in the receiver and the transmitter data paths.
SEMC Troubleshooting Manual
93
(124)