G3
Siemens Energy & Automation, Inc. 1000 McKee Street Batavia, Illinois 60510
SFIM-7002A-0901
Section G, September, 2001
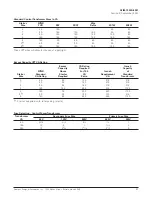
NEMA Wiring Types A, B, and C
NEMA types A, B, and C relate to type and location of field
terminations made on the motor Control Center.
Type A
User field wiring shall connect directly to device terminals
internal to the unit and shall be provided only on Class I motor
control centers.
Type B
B
Type B user field load wiring for combination motor con-
trol units size 3 or smaller shall be designated as B-d or
B-t, according to the following:
B-d connects directly to the device terminals, which are
located immediately adjacent, and readily accessible, to
the vertical wireway;
B-t connects to a load terminal block in, or adjacent to, the
unit.
B
Type B user field load wiring for combination motor con-
trol units larger than size 3, and for feeder tap units, shall
connect directly to unit device terminals.
B
Type B user field control wiring shall connect directly to
unit terminal block(s) located in or adjacent to each com-
bination motor control unit.
Type C
User field control wiring shall connect directly to master ter-
minal blocks mounted at the top or bottom of those vertical
sections that contain combination motor control units or con-
trol assemblies. Combination motor control units and control
assemblies shall be factory wired to their master terminal
blocks.
User field load wiring for combination motor control units size
3 or smaller shall connect directly to master terminal blocks
mounted at the top or bottom of vertical sections. Motor con-
trol unit wiring shall be factory wired to the master terminal
blocks.
User field load wiring for combination motor units larger than
size 3, and for feeder tap units, shall connect directly to unit
device terminals.
Basic Sections
- also referred to as the structure. This forms
the enclosure to house the bus and control units.
Horizontal (or Main) Bus
- may be mounted at the top, mid-
dle, or bottom of the control center depending upon the
design. This bus distributes power to multiple sections with
only one main power supply. Also the horizontal bus is a
means of tapping power for distribution to the various units
within a section.
Vertical Bus
(also referred to as the branch, feeder, or tap bus)
- its purpose is to distribute power to units within a section.
Horizontal Bus Support
- supports and insulates the hori-
zontal bus and is by design one of the factors determining the
maximum fault current bracing and limitation of the maximum
bus which may be utilized.
Vertical Bus Support
- maintains the vertical bus in its posi-
tion and provides a means of bracing the vertical bus for fault
currents. Design will limit the vertical bus size and configura-
tion.
Bus Barriers
- may be of insulating or non-insulating material
but, in either case they provide a means of isolating the bus
from accidental contact.
Channel Sills
(also referred to as mounting angles or sills for
base channels) - aid in the alignment of the motor control cen-
ter as well as providing a means of setting the motor control
center in place by grouting into the foundation or welding to
leveling plates.
Lifting Angles
(or eye bolts) - facilitate handling of the motor
control center at the job site when lifting by crane is required
to move the motor control center.
Unit Supports
- may be a shelf or divider angle, dependent
upon the design, but the main purpose is to divide the avail-
able space in the section into unit space as required for a par-
ticular arrangement. They also provide rigidity to the section
and are a means of gasket sealing.
Back Plates
- used to close off the rear of motor control cen-
ters assembled for front mounting only of units.
Top Cover Plates
- provide a means for closing the top of a
section; removable, when cutting conduit holes to eliminate
metal cuttings in the motor control center.
End Cover Plates
- close the openings in the the side sheets
at each end of a motor control center. These plates are easi-
ly removable for future addition to the motor control center.
Doors
- hinged covers to close off unit space and provide
“dead-front” construction as well as providing an easy
method to gain access to a unit. Doors are available in vari-
ous sizes and configurations dependent upon the require-
ments.
Units
- (also referred to as compartments or buckets) - con-
sist of all the components necessary to meet the require-
ments of an individual circuit. There are exceptions such as a
control power source which may be remote, pilot devices
grouped or remote, and control relays grouped into a master
relay panel. The units may be plug-in or fixed mounted. This
is normally determined by the unit requirements.
Plug-in construction means that the unit components are
mounted on an easily removable base which has stabs to
automatically engage the vertical power bus when the unit is
inserted into the proper location in the section.
Fixed mounted units are bolted into the allotted space within
the sections and fixed wired to the power bus.
Содержание TIASTAR SFIM-70020
Страница 63: ......
Страница 64: ......
Страница 65: ......
Страница 66: ......
Страница 67: ......
Страница 68: ......
Страница 69: ......
Страница 70: ......
Страница 71: ......
Страница 72: ......
Страница 73: ......
Страница 74: ......
Страница 75: ......
Страница 76: ......
Страница 77: ......
Страница 78: ......
Страница 79: ......
Страница 80: ......
Страница 81: ......
Страница 82: ......
Страница 83: ......
Страница 84: ......
Страница 85: ......
Страница 86: ......
Страница 87: ......
Страница 88: ......
Страница 96: ...4 ...
Страница 100: ...5 Today and tomorrow you ll know you have the very best ...
Страница 115: ...13 Siemens Energy Automation Inc ...
Страница 116: ...14 Siemens Energy Automation Inc ...
Страница 117: ...15 Siemens Energy Automation Inc ...