Application planning
3.5 Failure scenarios
S7-1500R/H redundant system
System Manual, 10/2018, A5E41814787-AA
87
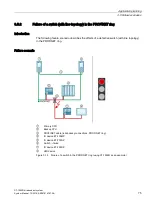
Sequence of events
1.
One of the two redundancy connections is interrupted.
2.
Availability is restricted. The redundant system will remain in the RUN-Redundant system
state.
3.
The primary CPU also fails. Due to the failure, the primary CPU is no longer visible for the
backup CPU.
4.
The redundant system does not switch to the backup CPU, probe switches to the STOP
system state. The role of the backup CPU remains unchanged.
Note
The backup CPU does not differentiate between the following scenarios:
•
It can no longer access the primary CPU because the latter has failed.
•
The other redundancy connection has also been interrupted and the primary CPU may
still be running.
That is why the backup CPU does not become the primary CPU. This prevents an
undefined system state.
5.
System redundancy has failed. The process is no longer controlled by the redundant
system.
Diagnostics
System state and operating states after the failure of the redundancy connection and primary
CPU:
●
Redundant system → STOP system state
●
Primary CPU → failed
●
Backup CPU → STOP operating state
–
MAINT LED → yellow light: The H
-system is not in the RUN-Redundant system state.
No partner CPU has been found in the H-system.
–
ERROR LED → flashes: IO devices cannot be accessed.
Note
To get detailed diagnostics information, evaluate the diagnostics buffer.
Solution
Replace the defective redundancy connection and the primary CPU. You can find additional
information on the procedure in the sections Replacing defective redundancy connections
(Page 261) and Replacing defective R/H CPUs (Page 260).
Содержание Simatic S7-1500H
Страница 1: ......