2BStructure and function
19BDetector
3
29 | 138
Building Technologies
007004_t_en_--
Fire Safety
2015-11-04
The following table shows the most important differences between the neural fire
detectors.
Type
Signal processing
Communication protocol
FDOOT221
Detection algorithms
●
FDnet
FDOOT241-8
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
●
MS8
FDOOT241-9
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
●
Collective
FDOOT241-A
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
FDOOT241-A3
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
●
AnalogPLUS
FDOOT241-A4
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
●
SIGMALOOP
FDOOT241-A5
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
●
Interactive
FDOOT241-A9
ASA
technology
●
FDnet
●
Collective
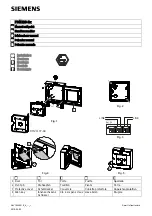
Structure and function
1 Heat sensors
3 Forward scatterer
2 Backward scatterer
4 Labyrinth
The detector has a sophisticated opto-electronic measuring chamber with two
optical transmitters, an optical receiver, and two thermal sensors.
The transmitters illuminate the smoke particles from different angles. One sensor
acts as forward scatterer, the other as backward scatterer. The scattered light then
hits the receiver (photodiode) and generates a measurable electric signal.
The combination of a forward and backward scatterer facilitates optimum detection
and the differentiation of light and dark particles, which leads to a homogenous
response behavior and optimizes the differentiation of wanted signals and
deceptive phenomena.
In addition, the heat sensors make it possible to detect fires without smoke
generation.
1
2
3
4