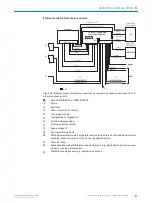
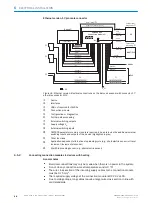
RS-232
!
"
§
Device
1
Host
TxD
RxD
GND
RxD
TxD
GND
RS-422
$
%
&
/
(
Device
1
Host
RD+
TD+
RD‒
TD‒
GND
TD+
RD+
TD‒
RD‒
GND
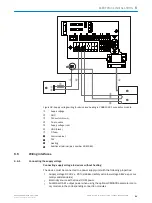
Figure 39: Internal circuitry for RS-232 and RS-485 data interfaces
1
Device
!
...
§
Pin assignment: See RS-232 pin assignment for the respective device
$
...
(
Pin assignment: See RS-422 pin assignment for the respective device
Termination of the RS-422 data interface
Termination of the data interface can be implemented in the connection module via
switches.
Additional information on this can be found in the operating instructions for the relevant
module.
6.6.3
Wiring the CAN interface
If the wiring of the CAN interface is carried out via a connection module, then the rele‐
vant operating instructions of the module used must be followed.
6.6.4
Wiring digital switching inputs
Physical switching inputs on the device
The physical switching inputs can be used for starting and/or ending the reading pulse
or for feeding an incremental signal.
Depending on the device, there are different number of switching inputs available on
the connections,
see "Pin allocation of the connections", page 43
Table 13: Characteristic data for the switching inputs
Switching behavior
Power at the input starts the internal reading interval of the device
(default: active high, debounce time: max. 10 ms)
Properties
Opto-decoupled
Reverse polarity protected
Electrical values
The electrical values are identical for all switching inputs.
Low: |V
in
| ≤ 2 V; |I
in
| ≤ 0.3 mA
High: 6 V ≤ |V
in
| ≤ 32 V; 0.7 mA ≤ |I
in
| ≤ 5 mA
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
6
8019588/129Z/2019-02-07 | SICK
O P E R A T I N G I N S T R U C T I O N S | CLV63x, CLV64x, CLV65x
53
Subject to change without notice