15 Basics
the PT-II system reaches a total modulation rate of 200/sec. The reason why differential
PSK is used on HF links is that signals are much too unstable and noisy (or with too large
a frequency error) to be used effectively by "normal" coherent PSK detectors.
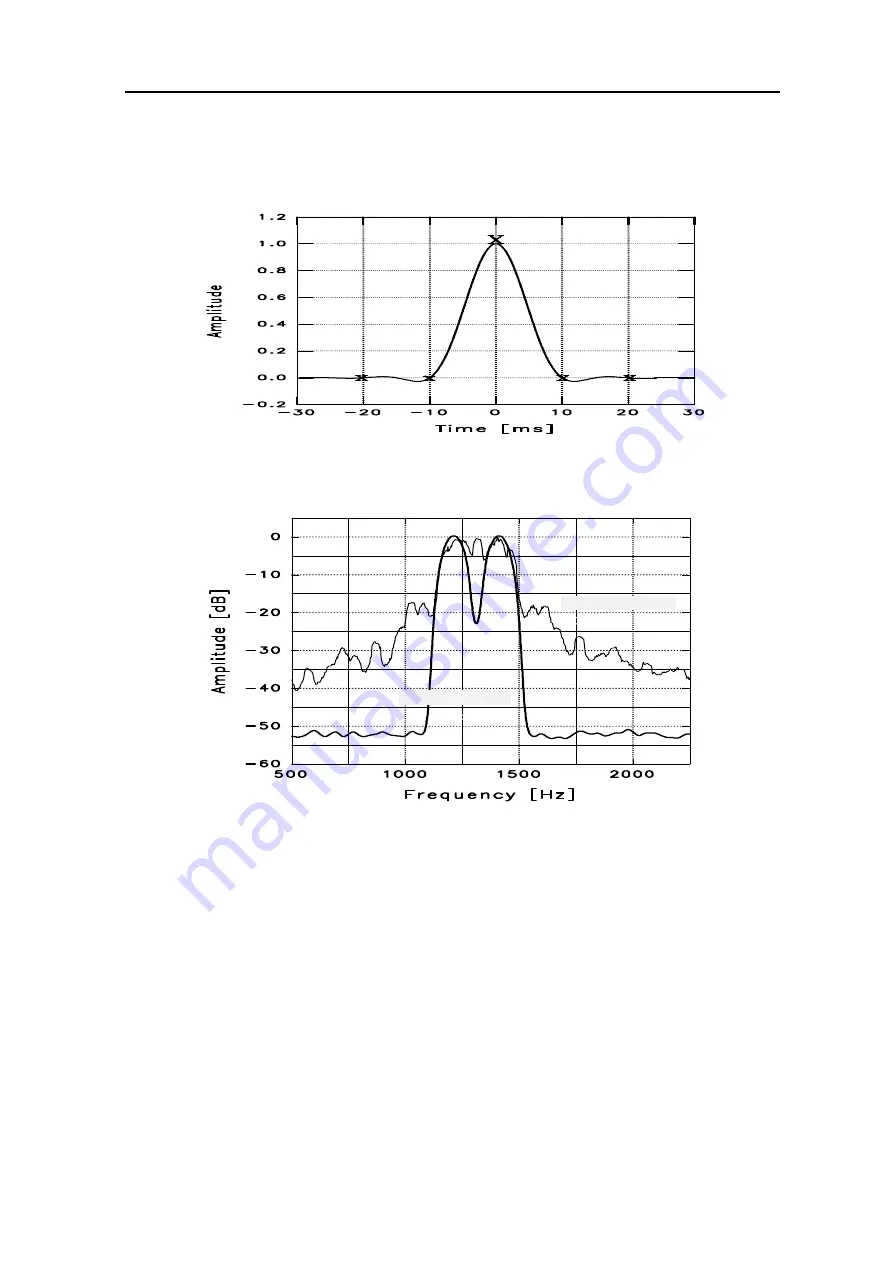
Figure 15.1: Raised-Cosine-Pulse, Sampling points marked X or x.
3 0 0 B d F S K
P A C T O R - I I
Figure 15.2:
PACTOR-II spectrum and 300 Bd FSK (200 Hz Shift)
For arguments sake, if there are only two possible phase changes between the steps it’s
called differential binary phase shift keying (DBPSK). Every step contains exactly one bit
of information. If four different phase changes are allowed, then the modulation is called
"differential quadrature phase shift keying" (DQPSK). Every step of course then carries
two bits of information. With eight or sixteen allowable phase changes, the modulation is
called 8-DPSK or 16-DPSK, each step containing three or four bits of information
respectively. The required signal to noise ratio, however, climbs rapidly, as the number of
allowable phase changes increases. Table 1 shows the total bit rates for the PT-II
modulation scheme (without data compression).
174
Содержание PTC-IIex
Страница 14: ...List of Figures and Tables XII...
Страница 30: ...3 Installation 16...
Страница 108: ...7 Audio 94...
Страница 126: ...8 FAX 112...
Страница 173: ...12 SYStest 159...
Страница 183: ...14 Circuit Description 169...
Страница 195: ...15 Basics 181...
Страница 201: ...B Technical Data 187...
Страница 202: ...C Layout Appendix C 19 Layout B 1 Motherboard Figure B 1 Motherboard 188...
Страница 203: ...C Layout 189...
Страница 215: ...Index 202...















































