41
SALICRU
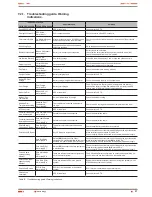
Models:
TWIN PRO
TWIN/3 PRO
≤
10 kVA
TWIN/3 PRO > 10 kVA
Available powers (kVA / kW)
4 / 3.6
5 / 4.5
6 / 5.4
8 / 7.2
10 / 9
8 / 7.2
10 / 9
12 / 10.8 15 / 13.5
20 / 18
Batteries
Voltage / capacity
12 V DC / 7 Ah
12 V DC / 9 Ah
12 V DC / 9 Ah
Quantity of batteries in serial / set voltage
20 / 240 V DC
24 / 288 V DC
Quantity batteries set
1
2
Low battery voltage, block / set
11.4 V DC / 228 V DC
11.4 V DC / 273.6 V DC
End battery voltage:
- From 0-30 % load, block / set
10.7 V DC / 214 V DC
10.7 V DC / 256.8 V DC
- From 30-70 % load, block / set
10.2 V DC / 204 V DC
10.2 V DC / 244.8 V DC
- From > 70 % load, block / set
9.5 V DC / 190 V DC
9.5 V DC / 228 V DC
Internal battery charger
Type of charge
I / U (Constant current / constant voltage)
Constant current / constant voltage
1 or 1.4 A depending on model / 273 V DC
(13.65 V DC block)
4 A / 345.6 V DC
(14.4 V DC block.)
Floating voltage, block / set
13.65 V DC / 273 V DC
13.65 V DC / 327.6 V DC
Maximum charging current
1 A
1.4 A
4 A
Recharging time
5 hours at 90%
Leakage current
< 500 µA
Voltage / temperature compensation
– 3 mV / ºC per battery annd above 25 ºC
Internal battery charger option (B1)
Maximum charging current
4 A
8 A
Generals
Communication ports
2 (RS232 -DB9- and USB, mutally exclusive)
Monitoring software
WinPower (free download)
Noise level at 1 m.
< 50 dB
< 55 dB
Operating temperature
0.. 45 ºC
Storage temperature
– 15.. + 50 ºC
Storage temperature without batteries
– 20.. + 70 ºC
Operating altitude
< 1000 m (for higher altitudes correct according to table 14)
Relative humidity
0-95 % non-condensing
Protection degree
IP20
Dimensions -Depth x Width x Height- (mm)
550 x 260 x 708
650 x 350 x 890
Weight (kg) -Standard UPS-
72
73
74
85
86
87
88
189
190
191
Weight (kg) -B0 version UPS-
14
15
16
26
27
28
29
58
59
60
Weight (kg) -B1 version UPS-
16
17
18
29
30
31
32
63
64
65
Safety
EN-IEC 62040-1; EN-IEC 60950-1
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
EN-IEC 62040-2
Marking
CE
Quality system
ISO 9001 and ISO 140001
Table 13.
General technical specifications.
Altitude (m.) 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 4500 5000
Power
100% 95%
91%
86% 82%
78%
74%
70%
67%
Table 14.
Power correction in relation to the working height.
8.2. Glossary.
•
AC.-
It is nominated as alternating current (abbreviation
in Spanish CA and in English AC) to the electrical current
in which the magnitude and direction varies in a cyclic
way. The most common wave shape of the alternating
current is sinewave, because the energy transmission
is better. Nevertheless, some applications could need
other period wave shapes, like triangular or square
•
Bypass.-
Manual or automatic, it is the physical junction be-
tween the input and the output electric device.
•
DC.-
The direct current (CC in Spanish, DC in English) is the
continuous electron flow through a cable between two points
with different potential. Unlike the alternating current, in direct
current the electrical loads always flow in the same direction
from the highest potential point to the lowest one. Although,
usually the direct current is identified with the constant cur-
rent (for example the one supplied by the battery), it is con-
tinuous any current that always maintain the polarity.
•
DSP.-
It is the acronym of Digital Signal Processor. A DSP is
a system based on a processor or microprocessor that has
instructions in it, a hardware and an optimised software to
develop applications where numerical operations are needed
with very fast speed. Due to this, it is very useful to process
analogical signals in real time: in a system that runs in this
way (real time) samples are received, usually coming from an
analogical/digital converter(ADC).
•
Power factor.-
It is defined as power factor, p.f., of an alter-
nating current circuit, as the ratio between the active power,
P, and the apparent power, S, or as the cosines of the angle
that make the current and voltage vectors, designating as
cos φ, being φ the value of that angle.
•
GND.-
The term ground, as its name states, refers to the po-
tential of the earth surface.
•
EMI filter.-
Filter able to decrease the electromagnetic inter-
ferences, which is the perturbation that happens in a radio
receptor or in any other electrical circuit caused by the elec-
tromagnetic radiation coming from an external source. Also
it is known as EMI, ElectroMagnetic Interference, Radio Fre-
quency Interference or RFI. This perturbation can derate or
limit the efficiency of the circuit.
Содержание SLC TWIN PRO Series
Страница 2: ......
Страница 43: ...43 SALICRU...