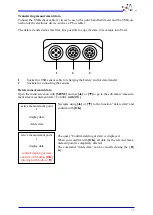
21
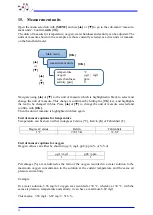
With regard to % Vol, the same calculation as above is used, merely with the factor 20.95, as
air contains 20.95% oxygen.
95
,
20
*
/
89
,
6
/
56
,
3
l
mg
l
mg
entration
oxygenconc
[%] = 10.82 % Vol
Unit of measure options for water hardness
Water hardness can either be shown in °dH, °fH, °eH, mmol/l, mval/l, mg/l, or ppm.
°dH
°fH
°eH
mmol/l
mval/l
mg/l
(CaO)
ppm
1
1,7848
1.2522
0.17832
0.35665
10
17.848
Salinity parameter options
Salinity is defined as (in simple terms) the salt content of a stretch of water, a body of water, or
water. This can be shown in PSU (Practical Salinity Unit) on the µdox hand-held meter, in
[psu]. PSU is a ratio.
Example:
Salinity (from the Latin salinitas) is defined as the salt content of a water-based liquid. In the
simplest case, it is shown as a mass share in g/kg (grammes of salt per kilogram of saline water
or solution), or in percent (1 % corresponds to 10g/kg). To determine the exact salt content, the
liquid must be evaporated and the residual salt content weighed. However, in practice, salinity
can also be determined using conductivity, whereby the measured conductivity of the unknown
salinity is determined against the conductivity of a defined potassium chloride solution of 32.4
g/l at 15 °C and air pressure of 1000 m/bar. If the water solution has the same conductivity as
the prescribed potassium chloride solution of 32.4 g/l, the ratio is 1, and this salinity is defined
as 35 psu.
On the µdox hand-held meter, salinity can be set between 1 and 50 psu in steps of 1 unit
(1,2,3,4...).
Examples of salinity levels of water-based liquids include:
Sea water approx. 35 …50 psu
Brackish water 0.5 …35 psu
Fresh water < 0.5 psu
Содержание udox
Страница 1: ...dox Operating instructions Version 1 6 8...
Страница 2: ......