MACTOOLS.COM
66
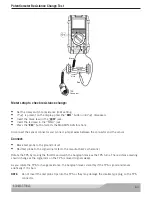
Pressure Sensor Tests
Recommended electrical test procedures for pressure sensors such as Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP)
and Barometric Pressure (BP) vary greatly depending upon type and manufacturer. Refer to the vehicle
manufacturer’s service manual for the schematics, specifications, and test procedures.
Analog Type Pressure Sensor.
Analog sensor can be tested using the voltage tests described for 3-wire
potentiometer. Use a vacuum pump to vary the pressure on the sensor in place of sweeping the sensor.
Digital Type Pressure Sensor.
A digital sensor can be tested by using the frequency (Hz) function of the meter
with the same series of tests suggested for 3-wire potentiometer voltage tests. Use a vacuum pump to vary the
pressure on the sensor in place of sweeping the sensor.
In all cases, refer to the vehicle manufacturer’s service manual for the correct testing procedures.
NOTE:
Resistance tests are impossible for pressure sensors because all pressure sensors have voltage or
frequency output.
Output Device (Actuator) Tests
The electrical tests for output devices varies depending upon type and manufacturer. Consult the vehicle
manufacturer’s service manual for the schematics, specifications, and test procedures.
Primary output devices generate a form of electromagnetic ON/OFF signal, which will generally be one of the
following three signals:
•
On or Off only (e.g., switches)
To check an on/off device such as a switch, perform continuity tests with the switch in the on and off
position.
•
Pulse width (e.g., fuel injectors)
Pulse width is the length of time an output device (actuator) is energized. To check fuel injectors, measure
the On time using the pulse width measurement function.
•
Duty cycle (e.g., mixture control solenoid)
Duty cycle (or duty factor) is the percentage of time a signal is above or below a trigger level during
one cycle. The amount of On time is measured as a percentage of the total On/Off cycle. To check a
mixture control solenoid, measure the percent of high (+) or low (-) time in a duty cycle. In most cases of
automotive electronics, the low (-) time is the On time.