246
•
Flexible service application
—Apply a service such as NAT or QoS to packets before or after they
are encrypted by IPsec. To handle packets prior to IPsec encryption, apply the service to the IPsec
tunnel interface. To handle IPsec encrypted packets, apply the service to the physical outbound
interface.
IPsec tunnel interface operation
IPsec encapsulation and de-encapsulation occur on IPsec tunnel interfaces.
shows how a clear
text packet arriving at a router is forwarded to the IPsec tunnel interface, encapsulated, and forwarded
out.
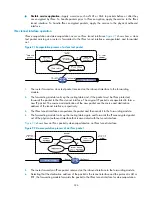
Figure 91
Encapsulation process of a clear text packet
1.
The router forwards a clear text packet received on the inbound interface to the forwarding
module.
2.
The forwarding module looks up the routing table and, if the packet must be IPsec protected,
forwards the packet to the IPsec tunnel interface. The original IP packet is encapsulated to form a
new IP packet. The source and destination of the new packet are the source and destination
address of the tunnel interface, respectively.
3.
The IPsec tunnel interface encapsulates the packet and then sends it to the forwarding module.
4.
The forwarding module looks up the routing table again and forwards the IPsec-encrypted packet
out of the physical outbound interface that is associated with the tunnel interface.
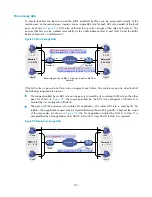
shows how an IPsec packet is de-encapsulated on an IPsec tunnel interface.
Figure 92
De-encapsulation process of an IPsec packet
5.
The router forwards an IPsec packet received on the inbound interface to the forwarding module.
6.
Detecting that the destination address of the packet is the tunnel interface and the protocol is AH or
ESP, the forwarding module forwards the packet to the IPsec tunnel interface for de-encapsulation.