321
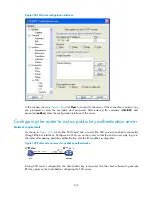
Likewise, to save the private key, click
Save private key
. A warning window appears to prompt you
whether to save the private key without any protection. Click
Yes
and enter the name of the file for
saving the key (
private.ppk
in this case).
Figure 111
Save the private key on the client
Then, you must transmit the public key file to the server through FTP or TFTP.
2.
Configure the SSH server.
# Generate RSA and DSA key pairs, and enable SSH server.
<Router> system-view
[Router] public-key local create rsa
[Router] public-key local create dsa
[Router] ssh server enable
# Configure an IP address for interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1, which the SSH client uses as the
destination for SSH connection.
[Router] interface GigabitEthernet 1/0/1
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] ip address 192.168.1.40 255.255.255.0
[Router-GigabitEthernet1/0/1] quit
# Set the authentication mode for the user interfaces to AAA.
[Router] user-interface vty 0 4
[Router-ui-vty0-4] authentication-mode scheme
# Enable the user interfaces to support SSH.
[Router-ui-vty0-4] protocol inbound ssh
# Set the user command privilege level to 3.
[Router-ui-vty0-4] user privilege level 3
[Router-ui-vty0-4] quit
# Import the client's public key from file
key.pub
and name it
Router001
.
[Router] public-key peer Router001 import sshkey key.pub
# Specify the authentication method for user
client002
as
publickey
, and assign the public key
Router001
to the user.
[Router] ssh user client002 service-type stelnet authentication-type publickey assign
publickey Router001