www.cooperbussmann.com/wirelessresources
Cooper Bussmann 915U-2 Wireless Mesh I/O and Gateway User Manual
9
Rev Version 1.2.2
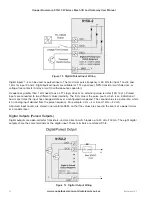
appear at any output on any module in the entire system.
Modules can be used as repeaters to re-transmit messages on to the destination module. Repeaters can repeat
messages on the radio channel or from the radio channel to the serial channel (or serial to radio). The meshing
protocol automatically selects other stations to act as repeaters if required (up to ten hops). If you configure the
module to use the legacy WIBNet protocol, up to five repeater addresses may be configured for each input-to-
output link. For more information about using WIBNet, see “Product Reconfiguration” on page 78.
The units can be configured using the MConfig Utility via Ethernet or USB, or by accessing the internal webpages
using a Web browser. The MConfig Utility is described in “4.2 MConfig Utility” on page 34. For Web-based
configuration, see “4.3 Web-Based Configuration Utility” on page 65.
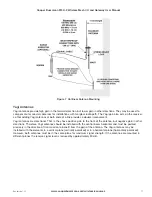
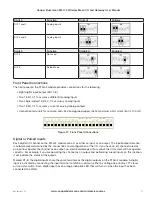
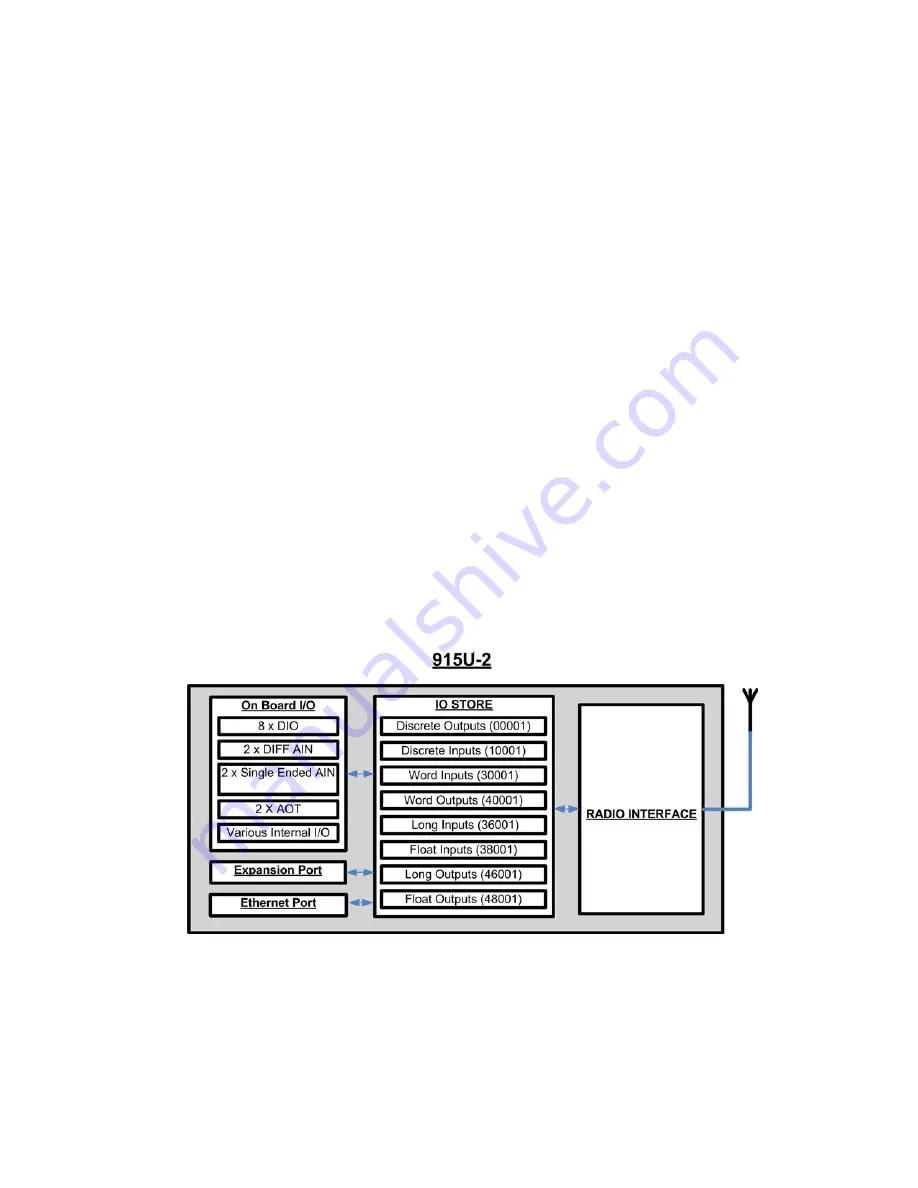
1.2 Module Structure
The 915U-2 module is made up of different areas that all interface with a central input and output storage area (I/O
store). The I/O store is an area of memory made available for the status of the physical on-board I/O and internal
I/O registers. It also provides services for other processes within the module.
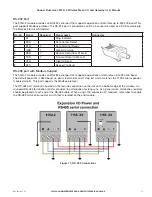
The I/O store is split into eight different blocks types:
• Two blocks made available for bit data (discrete)
• Two blocks made available for word data (analog)
• Two blocks made available for 32-bit words data (32-bit analogs)
• Two blocks made available for floating point data (floats)
Each of these block types in turn support input and output locations that can interface with the physical I/O on the
local machine and also be used for data storage when used as a gateway to external devices. These block type
locations are illustrated in Figure 1 and are described in Appendix B. There are other registers within the database
that can be used for system management.
Figure 1 Module Structure
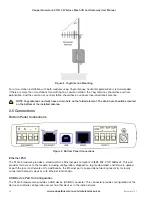
The Radio Interface (see Figure 1) allows the 915U-2 to communicate with other modules within the system using
a proprietary radio protocol called WIBMesh. I/O Messages from other 915U-2 modules are received on the radio
port and then passed to the I/O store which will in turn update the register locations accordingly. The WIBMesh
protocol is designed to provide reliable radio communications on an open license-free radio channel. It is an
extremely efficient protocol for radio communications because the messages are sent using exception reporting
(only transmitting when there is a change of an input signal) rather than transmitting all of the time. Update
messages can also be configured at a predetermined time for integrity checks.