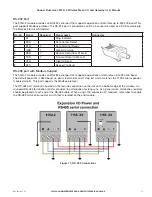
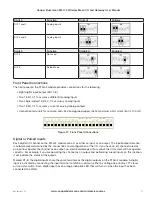
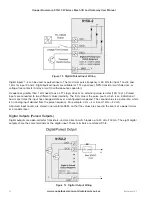
14
www.cooperbussmann.com/wirelessresources
Cooper Bussmann 915U-2 Wireless Mesh I/O and Gateway User Manual
Rev Version 1.2.2
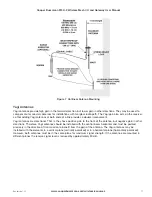
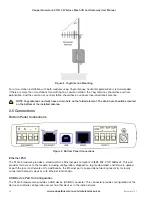
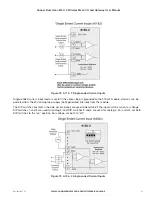
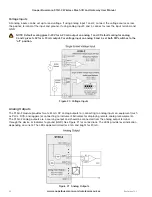
Figure 5 Grounding
2.3 Radio
The following radio variants are available in the 915U-2, depending on the country of operation.
900 MHz Spread Spectrum Radio
The radio uses frequency hopping spread spectrum modulation, which is a method of transmitting radio signals by
switching the carrier among many frequency channels using a pseudo-random sequence, called a hopset. There
are two hopsets that cycle through the sequence and switch to a different channel after each radio transmission.
Each hopset uses a different pseudo-random sequence of 50 channels.
The radio operates in the 902–928 MHz ISM band, which is split into two frequency bands, 902–914 MHz (low) and
915–928 MHz (high). In the United States and Canada, the 915U-2 can use both high and low bands. However, in
other countries, such as Australia, only the 915–928 MHz band is available.
Some countries use fewer channels. For example, New Zealand uses 18 channels in the frequency band 922.75–
927.00 MHz. In countries that allow the two bands to be used, the frequency band can be changed by using the
MConfig Utility and selecting the hopset on the Radio Settings screen for the module. The hopset only displays the
frequency bands available for the model and country. For details, see “Radio Settings” on page 69.
The receiver is continually scanning all channels within the hopset, and when a valid data packet is received it locks
on to the channel and receives the data.
A spread-spectrum transmission offers the following advantages over a fixed-frequency transmission:
• Spread-spectrum signals are more resistant to narrow-band interference
• Spread-spectrum signals are difficult to intercept or eavesdrop because of the pseudo-random transmission
sequences
• Transmissions can share a frequency band with other types of conventional transmissions with minimal
interference
869 MHz Fixed Frequency Radio
The 869 MHz fixed frequency radio operates in the unlicensed fixed frequency band of 869 MHz and is used in
Europe. There are two frequencies. The first operates at 869.525 MHz with a maximum transmit power level of
500 mW, and is regulated with a 10% duty cycle on the channel. This duty cycle limit requires that the module not
transmit for more than 10 % of the total operating time, which means other users of the unlicensed frequency are
able to transmit without interference. The second frequency operates at 869.875 MHz with a transmit power level
of 5 mW and no duty cycle regulation on the channel, which means the module can freely transmit as often as is
needed.
NOTE Care must be taken to ensure that the duty cycle limit is not exceeded when using the 869.525 MHz
frequency.