EXAMPLE:
Heat value = 980 Btu/cu ft
Specific gravity = 0.58
Therefore; Orifice No. 42 *
Manifold pressure 3.5-in. wc
* The furnace is shipped with No. 44 orifices. Therefore, in
this example all main burner orifices must be changed and
the manifold pressure must be adjusted.
(7.) Proceed to item c. to adjust manifold pressure.
b. Check gas input rate by clocking gas meter.
(1.) Obtain average yearly heat value for local gas
supply.
NOTE:
Be sure heating value of gas used for calculation is
correct for altitude. Consult local gas utility for altitude adjustment
of gas heating value.
(2.) Turn off all other gas appliances and pilots.
(3.) Start furnace and let run for 3 minutes.
(4.) Measure time (in sec) for gas meter to complete 1
revolution.
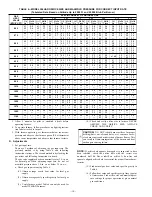
(5.) Refer to Table 7 for cu ft of gas per hr.
(6.) Multiply gas rate (cu ft/hr) by heating value (Btu/cu
ft).
EXAMPLE:
Btu heating input = Btu/cu ft X cu ft/hr
Heating value of gas = 1070 Btu/cu ft
Time for 1 revolution of 2-cu ft dial = 72 sec
Gas rate = 100 X 1070 = 107,000 Btuh
(7.) Measured gas input should not exceed gas input on
unit rating plate.
(8.) Proceed to item c. to adjust manifold pressure.
c. Adjust gas input.
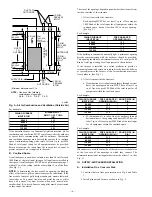
(1.) Remove regulator adjustment seal cap. (See Fig.
12.)
(2.) Turn adjusting screw counterclockwise to decrease
input. Turn screw clockwise to increase input. DO
NOT set manifold pressure less than 3.2-in. wc or
more than 3.8-in. wc for natural gas. Make any
major adjustments by changing main burner ori-
fices.
(3.) When correct input is obtained, replace regulator
seal cap. Main burner flame should be clear blue,
almost transparent. (See Fig. 13.)
d. High altitudes—In the U.S.A., gas input on rating plate
is for altitudes up to 2000 ft. Ratings for altitudes over
2000 ft must be 4 percent less for each 1000 ft above sea
level. To obtain the adjusted altitude rating, adjust the
manifold pressure, item c., and replace the main burner
orifice as needed. Refer to NFGC Appendix F, Table F-4
for proper orifice sizing at high altitudes.
e. Canadian installations only—The Canadian ratings are
approved for altitudes up to 2000 ft for natural and
propane gases. High-altitude ratings are from 2001 ft to
4500 ft above sea level. High-altitude input ratings
include a 10 percent derate as required by Canadian
standards. (See Table 8.)
2. Set temperature rise.
Do not exceed the temperature rise range specified on the
unit rating plate. Determine the air temperature rise as
follows:
a. Place duct thermometers in return and supply ducts as
near furnace as possible. Be sure thermometers do not
"see" heat exchangers so that radiant heat will not affect
thermometer readings. This is particularly important
with straight-run ducts.
b. When thermometer readings stabilize, subtract return-air
temperature from supply-air temperature to determine
temperature rise.
c. Adjust air temperature rise by adjusting blower speed.
Increase blower speed to reduce temperature rise. De-
crease blower speed to increase temperature rise.
Fig. 12—Redundant Automatic Gas Control Valve
A89171
PILOT
OFF
ON
THERMOCOUPLE
CONNECTION
PILOT
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW
MANUAL
ON/OFF
KNOB
INLET
PRESSURE
TAP
PILOT TUBE
CONNECTION
MANIFOLD
PRESSURE
TAP
REGULATOR
ADJUSTMENT
SEAL CAP
Fig. 13—Burner Flame
A84076
BURNER FLAME
PILOT FLAME
BURNER
MANIFOLD
—11—