Preface
MicroLogix 1000 Programmable Controllers User Manual
E–24
Pick and Place Machine Example
The following application example illustrates how the controller high-speed counter
is configured for the up and down counter using an encoder with reset and hold. For
a detailed explanation of:
•
XIC, XIO, OTE, RES, OTU, OTL, and TON instructions, see chapter 6.
•
GRT and NEQ instructions, see chapter 7.
•
MOV instruction, see chapter 9.
•
HSC and HSL instructions, see chapter 12.
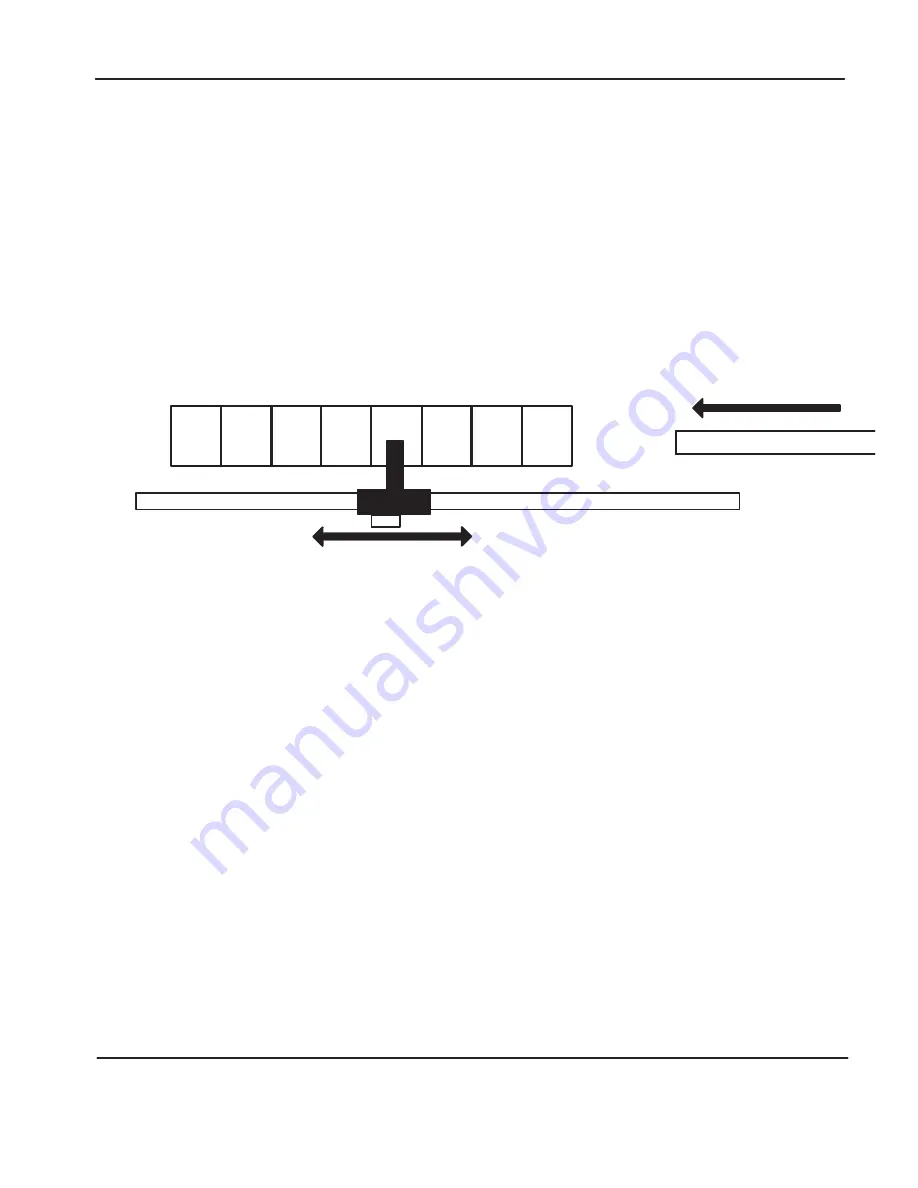
A
Gripper O:0/0
Conveyor
B
C
D
E
G
F
H
Rail
Encoder
A – I:0/0
B – I:0/1
C – I:0/2
Master PLC Outputs
Wired to Inputs:
I:0/5
I:0/6
I:0/7
Home Position
Storage Bins
Pick and Place Machine Operation Overview
A pick and place machine takes parts from a conveyor and drops them into the
appropriate bins. When the pick and place head is positioned over the conveyor
with a gripped part, the master PLC communicates to the controller controlling the
gripper which bin to drop the part into. This information is communicated by
energizing three outputs that are wired to the controller’s inputs. Once the controller
has this information, it grabs the part and moves down the rail. When the gripper
reaches the appropriate bin, it opens and the part falls into the bin. The gripper then
returns to the conveyor to retrieve another part.
The position of the pick and place head is read by the controller via a 1000 line
quadrature encoder wired to the controller’s high-speed counter inputs. When the
gripper is in the home position, the Z pulse from the encoder resets the high-speed
counter. The number of pulses the head needs to travel to reach each bin location is
stored in a data table starting at address N7:10 and ending at N7:17. The controller
uses indexed addressing to locate the correct encoder count from the data table and
load the information into the high preset of the high-speed counter.
efesotomasyon.com - Allen Bradley,Rockwell,plc,servo,drive
















































