Features and capabilities
16
Z-Edge 64 Configuration Guide
addresses. Since the addresses are used internally only, there is no possibility
of conflict with IP addresses used by other companies and organizations.
DHCP
The Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) provides a mechanism through
which client computers using TCP/IP can obtain configuration parameters
(such as the default router and the Domain Name System [DNS] server,
subnet mask, gateway address, and lease time) from a centrally located DHCP
server. DHCP dynamic reconfiguration requires a DHCP server, a forwarding
agent in each router, and DHCP capability in each client TCP/IP stack. The
most important configuration parameter carried by DHCP is the IP address.
Dynamic addressing allows a device to have a different IP address every time
it connects to the network, and in some systems, the device IP address can
change while it is still connected to the network. DHCP also supports a mix of
static and dynamic IP addresses.
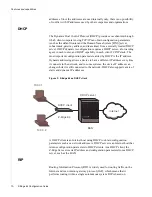
Figure 3: Z-Edge 64 as DHCP client
A DHCP client is an Internet host using DHCP to obtain configuration
parameters such as a network address. A DHCP server is an Internet host that
returns configuration parameters to DHCP clients. As a DHCP client, the
Z-Edge 64 receives its IP address and configuration parameters from a DHCP
server, such as the BAN.
RIP
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is widely used for routing traffic on the
Internet and is an interior gateway protocol (IGP), which means that it
performs routing within a single autonomous system. RIP is based on
Internet
BAN
Z-Edge 64
DHCP server
DHCP client
10.0.0.2
10.0.0.1